|
A New View on Exponential Functions
In one of the modules in this course, you examine the properties and characteristics of exponential functions. The general form of the exponential function is:
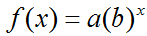
where a is the leading coefficient and b is the base to which the variable exponent is applied.
When you create a table of values for exponential functions, you may identify a pattern. Consider the function
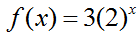
A table of values, for x values consisting of some positive integers, is as follows:
Table of values
| x | f(x) |
| 1 |
6 |
| 2 |
12 |
| 3 |
24 |
| 4 |
48 |
| 5 |
96 |
Do you see a pattern? Each successive term is the preceding term multiplied by the base. These function values, produced when the domain is limited to the positive integers, constitute a sequence with a distinct pattern: each term is determined by multiplying the preceding term by the base.
In the next topic, we will examine sequences with the pattern of a constant multiplier between terms. These sequences are called geometric sequences, and the constant multiplier is called the common ratio.
|
