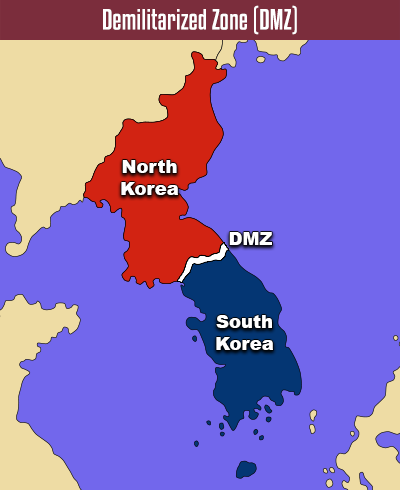
East Asia
East Asia

East Asia extends from the interior of the Asian continent to the Pacific coast. It also includes several islands and peninsulas. From ancient civilizations to modern global economies, the countries of East Asia have played important roles in human history. In this interactivity, you will explore the countries of China, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, North Korea, and Mongolia. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Religious Diversity in East Asia
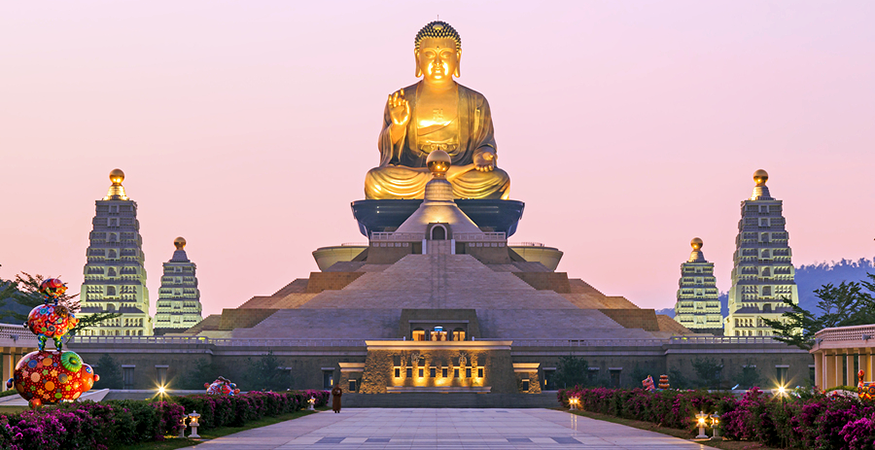

Statue of Buddha at a temple in Taiwan
Several different religions are practiced throughout East Asia. Some of the most common are Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Shintoism, Christianity, and Islam. During the third century A.D. (C.E.), Buddhist missionaries traveled the Silk Road and brought their religion from India to China. Over time, Chinese monks spread Buddhism to the rest of East Asia. Buddhism was often merged with other East Asian religions. Muslim traders brought Islam to northwestern China during in the eighth century A.D. (C.E.). In the 1600s, Christianity was spread throughout East Asia by missionaries.
Confucianism
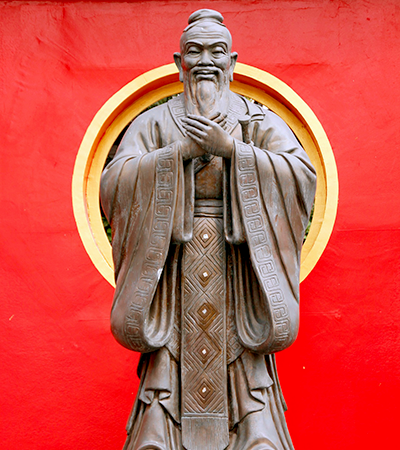

Statue of Confucius in China
Confucius was a teacher, politician, and philosopher from ancient China. He lived from 551-479 B.C. (B.C.E.). Confucianism is a system of ethics based on his philosophies. Some of the main tenets are the belief that humans are good, and respectful social relationships are essential for peace. Additionally, Confucianism values education, respect for elders, and ancestor worship. Confucianism has influenced Chinese and East Asian culture for thousands of years. It is often practiced along with Buddhism or Taoism.
Taoism
Taoism is a philosophical belief system that began in ancient China. It is believed that Taoism was developed by Lao Tzu. He taught that humans could achieve peace, harmony, and health by following the Tao, which means “the way.” Taoist philosophy is often symbolized by the yin-yang symbol. The yin-yang represents balanced opposites, like male and female or dark and light. Like Buddhists, some Taoists worship in pagodas.
Shintoism
Shintoism is native to Japan. Followers of this religion practice ancestor worship and believe in a sacred essence. They believe that spirits exist throughout nature, and these spirits can be manifested in various forms. For instance, spirits can exist in people, animals, rivers, trees, and rocks. Many people in Japan practice Shintoism along with Buddhism.
Cultural Influences of East Asia

East Asia is a culturally diverse region that is home to a variety of religions, languages, and traditions. The cultural influences of East Asia can be traced back to some of the oldest civilizations in the world. Over time, these influences have created a unique cultural landscape. In this interactivity, you will explore the cultural influences of East Asia. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Economic Characteristics of East Asia
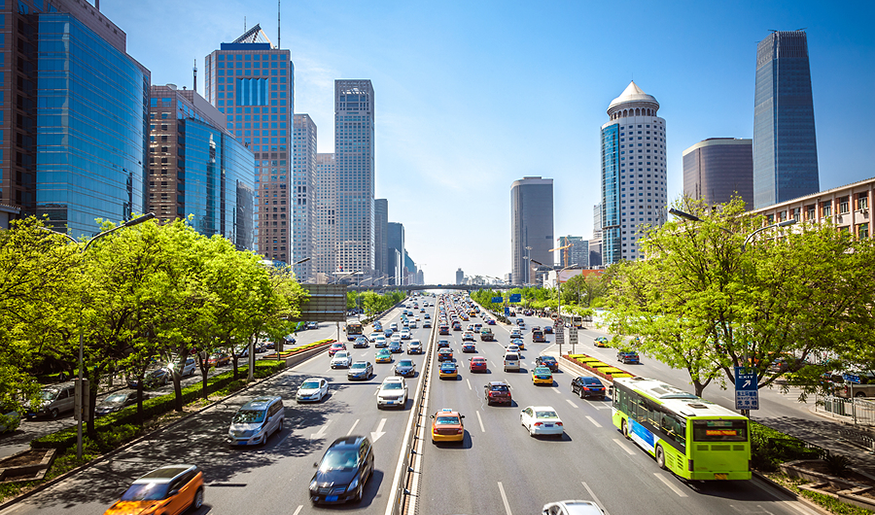

Central Business District of Beijing, China
The People’s Republic of China is technically a developing country; however, it has the second largest economy in the world, after the United States. Beginning in the 1980s, China began to make economic reforms. The Chinese economy began to transition from a centrally planned economy to a free market economy. Trade was opened up to foreign countries for the first time since the Chinese Communist Revolution. The country has experienced rapid economic growth and has become a shipping magnate. This means the country has made a lot of money from shipping and international trade.
China is one of the world’s leaders in industrial production. Machinery, electronics, textiles, and other manufactured goods are produced and exported. China is also the world’s largest producer of agricultural goods. The country has abundant arable land that is used to grow rice, wheat, and soybeans. Additionally, the Chinese fishing industry accounts for roughly one-third of all fish production. China does not export these agricultural goods. Instead, it uses them to feed its large population.
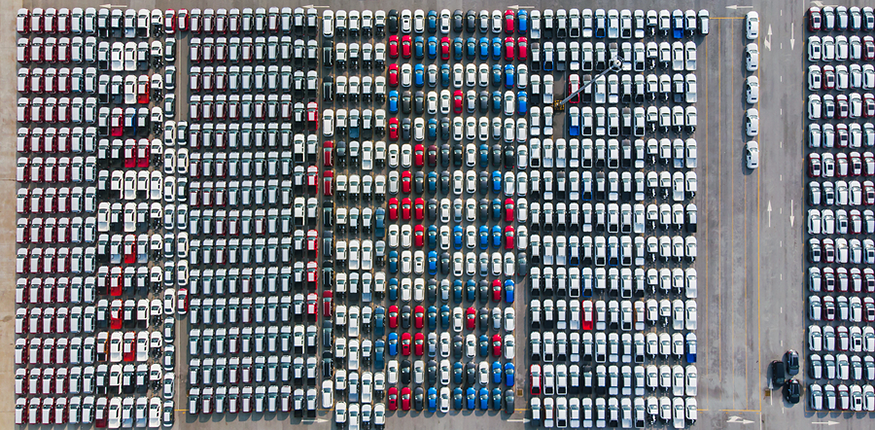

Newly manufactured Japanese cars waiting for export
Although Japan lacks abundant natural resources, it is a highly developed country. It has the third largest GDP in the world, and is an important part of the global economy. Japan has a well-developed infrastructure and a highly skilled workforce. It has a large automotive industry that produces cars and other vehicles. The country also manufactures electronics, computers, and other high-tech goods. Like other developed nations, Japan has a large tertiary sector. Around two-thirds of the population have service jobs.
South Korea and Taiwan share many economic characteristics with Japan. They are both highly developed countries with high standards of living. They also lack many of the natural resources needed to support a developed economy. Because of this, South Korea and Taiwan are heavily involved in international trade. Major exports include electronics, computers, and smartphones. They also manufacture automobiles and ships. Like Japan, many people in South Korea and Taiwan work in service jobs.
East Asia Review
 Now that you have learned about the major regions, cultural influences, and economic characteristics of East Asia, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.
Now that you have learned about the major regions, cultural influences, and economic characteristics of East Asia, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.