Cultural Regions
A cultural region is a geographic area defined by a common cultural characteristic. This could include language, economics, ethnicity, politics, or religion. Borders of a cultural region are sometimes unclear. Multiple cultural regions may even overlap.
People generally identify with the cultural region where they were born. Individuals from different parts of the world might also bond over cultural similarities. In contrast, cultural differences can create conflict between people living in the same area.
Cultural Regions Based on Language

A shared language allows people to communicate, which helps unite them culturally. Conversely, speaking different languages may divide people. In this interactivity, you will learn more about cultural regions based on language. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Cultural Regions Based on Ethnicity

Ethnicity refers to the shared cultural characteristics of a group of people. It encompasses the ancestry, art, customs, food, history, language, nationality, and religion of a culture. In this interactivity, you will examine the impact of ethnic heritage on cultural regions. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Cultural Regions Based on Religion

Throughout history, religious traditions have unified people through a shared cultural identity. However, these same religions have also created deep divisions and caused conflict. In this interactivity, you will explore the major world religions. You will also examine how religions can unify or divide regions. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Architecture

Architectural structures reveal a lot about the culture that built them. For example, religious buildings reflect a region's cultural characteristics. Some religious buildings include churches, mosques, pagodas, synagogues, and temples.
Also, you can learn a lot about a culture by considering size, shape, and building materials used in dwellings, or houses. For example, what type of society might have rectangular-shaped dwellings with long-lasting materials? Likely, these homes are in a complex society with permanent settlements and agriculture. Hunter-gatherer and nomadic cultures tend to have curve-shaped dwellings. The materials are lighter and easily break down.
Changes in Perception
The way people view and understand a cultural region can change over time. As regional labels shift, people's perception of the area changes. This is exemplified by two regions found in the United States: the Rust Belt and the Sun Belt.
The Rust Belt
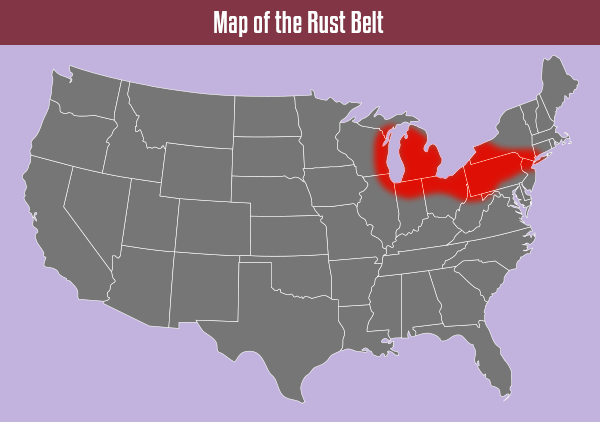
Map of the Rust Belt: Detailed Description
The term, Rust Belt, describes a deindustrialized region in Northeastern United States. The name Rust Belt developed when the region experienced a significant economic decline. Before this shift, people called this area the Factory Belt or the Steel Belt. These names came about because of a large amount of industrial manufacturing. In the late twentieth century, manufacturing jobs started to disappear. This increased unemployment, crime, and debt in the region.
The Sun Belt
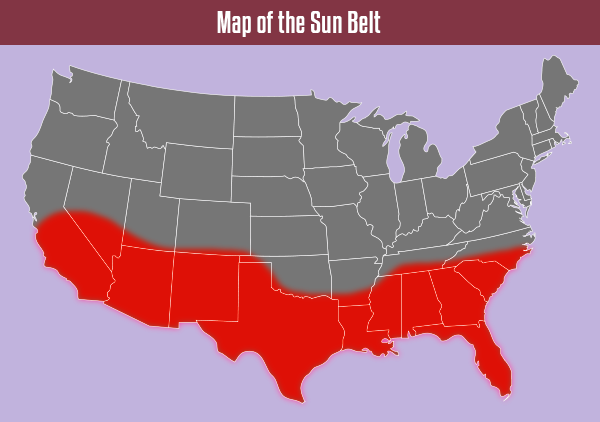
Map of the Sun Belt: Detailed Description
The Sun Belt is a term used to describe the Southeast and Southwest United States. The region experienced significant economic and population growth in the 1960s and 1970s. New farming technologies helped increase agriculture, and air conditioning made the heat manageable. This allowed industries like aerospace, defense, and oil to develop in the region. People from inside and outside the U.S. migrated to the Sun Belt in search of economic opportunities. Similarly, a large part of the retirement population moved to the Sun Belt.
Cultural Regions Review

 Now that you have learned about the characteristics of a cultural region, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.
Now that you have learned about the characteristics of a cultural region, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.









