Physical Geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia
Physical Features of North Africa and Southwest Asia

North Africa and Southwest Asia are located where Africa, Asia, and Europe meet. This region is also known as the Middle East. In this interactivity, you will explore the major physical features that characterize this large region. This includes peninsulas, deserts, seas, rivers, and mountains. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Climate Regions
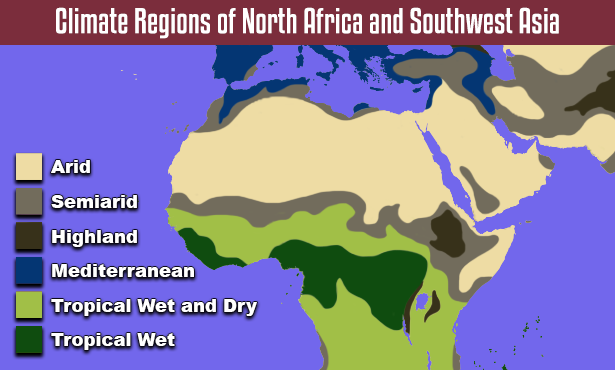
Climate Regions of North Africa and Southwest Asia: Detailed Description
Most of North Africa and Southwest Asia has an arid desert climate. The Sahara covers most of North Africa, from the Atlantic Ocean to the Red Sea. The Arabian Desert covers the majority of the Arabian Peninsula. These deserts are vast, dry, and inhospitable to most vegetation. Some cacti and drought-resistant shrubs with deep roots are able to survive the lack of precipitation.

Semiarid climate region in Morocco
Semiarid climate regions are found along the outer edges of the arid climate regions. Semiarid climate regions receive more rainfall than arid climate regions. However, drought is a common risk. Semiarid climate regions have large areas of steppe with a few trees. In North Africa, this region is found north and south of the Sahara. In Southwest Asia, it is found on the southwest corner of the Arabian Peninsula, and on the Anatolian and Iranian plateaus.
The Mediterranean climate can also be found in North Africa and Southwest Asia. A Mediterranean climate has mild temperatures. The summers are usually dry, with most of the rain falling during the winter months. This climate region supports chaparral vegetation. In North Africa, this type of region can be found along the Mediterranean coast. The largest region in North Africa is located north of the Atlas Mountains. In Southwest Asia, this region can be found along the coast of the Anatolian Peninsula and the eastern Mediterranean. It can also be found near the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers.
Water Resources
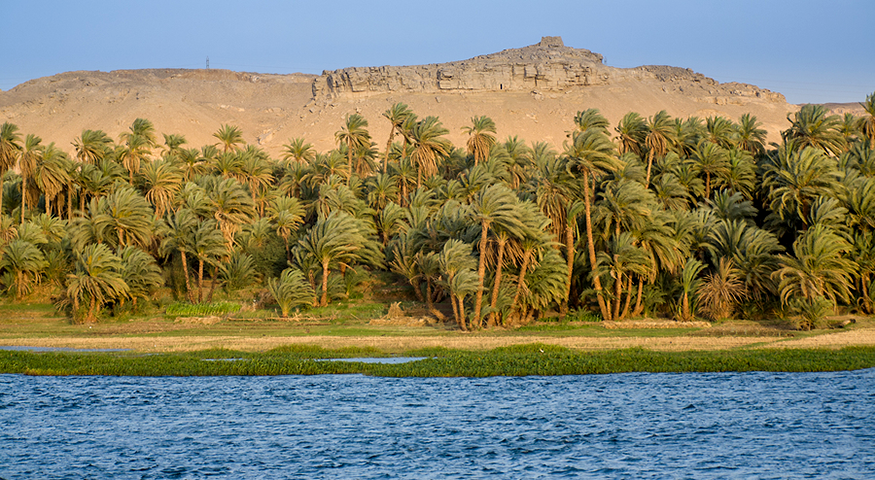

The Nile River in Egypt
The arid climate of North Africa and Southwest Asia limits human settlement and agriculture. Freshwater is a valuable resource in the region. As a result, most of the population is concentrated near rivers. These rivers provide freshwater and fertile soil. The major rivers of this region are the Nile, Jordan, Tigris, and Euphrates.
The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers experience seasonal flooding. During the warm summer months, snow accumulated in the Taurus Mountains begins to melt. This increases the water levels of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, causing them to flood. The flooding allows irrigation. It also deposits alluvial soil along the river banks. Alluvial soil is fertile soil or sediment that is deposited by a flowing river. It is typically found in flood plains near a river, or in a delta at the mouth of a river. Before the Aswan High Dam was built in the 1960s, the Nile River and the Nile Delta also experienced seasonal flooding.

A wadi in Oman
In addition to rivers, oases and wadis provide water in this arid region. An oasis is a fertile area with water found in a desert. The water in an oasis comes from natural springs located underground. Oases range in size. Some oases support a few trees while others are large enough to support cities and agriculture. A wadi is a valley or riverbed that is usually dry, except when it rains. Wadis fill with water during the rainy season in North Africa and Southwest Asia. Wadis provide temporary access to water. However, the flooding makes them unpredictable and potentially destructive.
Physical Geography of North Africa and Southwest Asia Review

![]() Now the you have learned about the major physical regions, landforms, and water features of North Africa and Southwest Asia, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.
Now the you have learned about the major physical regions, landforms, and water features of North Africa and Southwest Asia, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.
