Mesopotamia
Background of Mesopotamia

About 3,300 B.C. (B.C.E.), Mesopotamia became home to the first River Valley Civilization, Sumer, which is located in present-day Iraq and Kuwait. While this location is currently in the middle of a desert, during ancient times, it was a bustling port on the Euphrates River. In this interactivity, you will learn about various aspects of Mesopotamia. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
 Due to its location between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Mesopotamia is called "the land between two rivers." Also known as the Fertile Crescent, Mesopotamia thrived in this region heavily due to the river valleys in which the Sumerian, Babylonian, and Assyrian people settled, because all three of these civilizations depended on the rivers' water for survival. Take a moment to view the video, Timelines of Ancient Civilizations: Mesopotamia - Part I, from eMediaVASM, to further explore how the first villages in Mesopotamia flourished. As you watch, take note of why it was important that the rivers washed soil out of the surrounding mountains, and how it led to the invention of irrigation, and provided fertile soil for growing crops. Also, consider whether there was a downside to living near the rivers.
Due to its location between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Mesopotamia is called "the land between two rivers." Also known as the Fertile Crescent, Mesopotamia thrived in this region heavily due to the river valleys in which the Sumerian, Babylonian, and Assyrian people settled, because all three of these civilizations depended on the rivers' water for survival. Take a moment to view the video, Timelines of Ancient Civilizations: Mesopotamia - Part I, from eMediaVASM, to further explore how the first villages in Mesopotamia flourished. As you watch, take note of why it was important that the rivers washed soil out of the surrounding mountains, and how it led to the invention of irrigation, and provided fertile soil for growing crops. Also, consider whether there was a downside to living near the rivers.
The Assyrian Empire
The Assyrian Empire was a large but short-lived empire in Mesopotamia. The height of the Assyrian Empire lasted from 700 B.C. (B.C.E.) until around 612 B.C. (B.C.E.), when it was conquered by the Chaldeans and the Medes people. Use the map below to examine the extent of the Assyrian Empire.
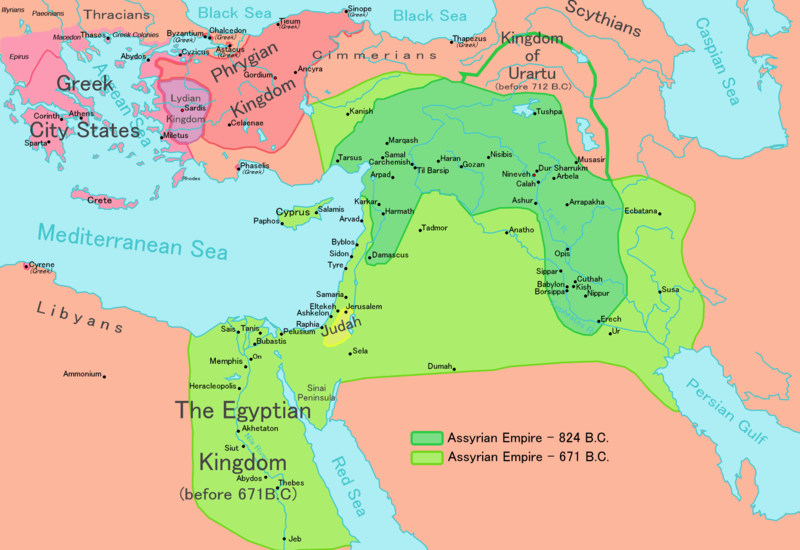
Map of the Assyrian Empire
The Assyrian Empire was organized into regional governorships that were ruled by a king. In addition, the Assyrians had an effective military and used iron weapons. The army was well organized, and soldiers were categorized into a hierarchy of different roles and duties. Assyrian armies destroyed structures and farms in the lands they captured. Also, they tortured the populations in these lands.
Babylon

An artist's depiction of the Hanging Gardens of BabylonBabylon was an ancient city-state located in Mesopotamia in what is present-day Iran. After the collapse of the Assyrian Empire, Babylon became the capital of the empire, and was ruled by Nebuchadnezzar II from 605 B.C. (B.C.E.) to 562 B.C. (B.C.E.). During this time, Nebuchadnezzar led the Chaldeans in the invasion of the Kingdom of Israel and Kingdom of Judah. This invasion was responsible for the exile of the Jews from Israel. In addition, Nebuchadnezzar II was responsible for building the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, a palace complex full of exotic trees and plants. Today, the Hanging Gardens of Babylon are considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Mesopotamia Review

 Now that you have learned about Mesopotamia, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.
Now that you have learned about Mesopotamia, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.




