Ancient Egypt
Geography and the Nile River
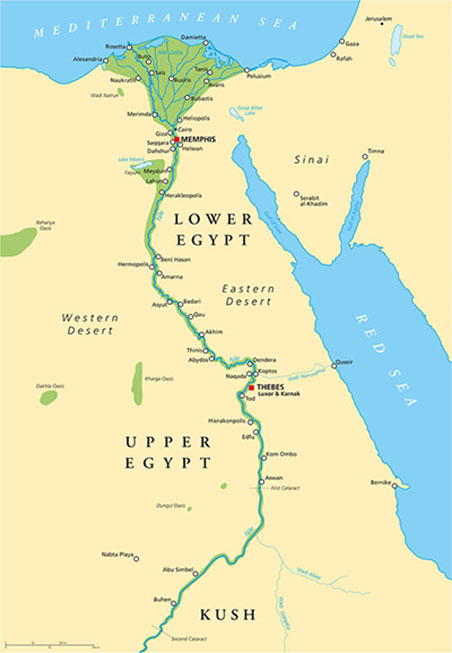 Ancient Egyptian civilization was located in northeast Africa, and centered along the Nile River, the longest river in the world. Without the Nile River, Egypt would exist as a barren desert. Specifically, the Nile River stretched from Lake Victoria in the south, in what was called Upper Egypt; it flowed into the Nile River Delta in the north, in what was called Lower Egypt, and emptied into the Mediterranean Sea. In the image, notice how the Nile River Delta is triangular-shaped. It is actually marshland formed by deposits of fertile soil found at the mouth of the Nile River. Egyptians relied on the yearly flooding to produce nutrient-rich soil, which enabled them to grow crops and become prosperous. Fortunately, natural boundaries around ancient Egypt, like the Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, and a variety of deserts, served as barriers against threats from outside invaders.
Ancient Egyptian civilization was located in northeast Africa, and centered along the Nile River, the longest river in the world. Without the Nile River, Egypt would exist as a barren desert. Specifically, the Nile River stretched from Lake Victoria in the south, in what was called Upper Egypt; it flowed into the Nile River Delta in the north, in what was called Lower Egypt, and emptied into the Mediterranean Sea. In the image, notice how the Nile River Delta is triangular-shaped. It is actually marshland formed by deposits of fertile soil found at the mouth of the Nile River. Egyptians relied on the yearly flooding to produce nutrient-rich soil, which enabled them to grow crops and become prosperous. Fortunately, natural boundaries around ancient Egypt, like the Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, and a variety of deserts, served as barriers against threats from outside invaders.
Some uncertainty exists about the transition of early Egypt from a series of villages into a unified kingdom. Most agree, however, that Egypt was unified into a singular kingdom around 3,000 B.C. (B.C.E.) by an ambitious man named Menes. Initially Menes rose to power in Upper Egypt, but he extended his authority into Lower Egypt around the Nile River Delta. In addition, Menes founded the city of Memphis, located near modern-day Cairo. Memphis became the cultural and political center of ancient Egypt.
The Pharaohs

Statue of Pharaoh Khufu in the
Cairo Egyptian Museum
The king of Egypt, referred to as the pharaoh, had great power. In fact, Menes, who you learned about in the previous section, became an Egyptian pharaoh. The position of pharaoh was hereditary; when one pharaoh died, his son or closest descendant inherited the right to rule. Pharaohs acquired a godlike status, and played a significant role in politics and religion. In this way, ancient Egypt was a
theocracy, because the Egyptians believed the pharaoh received the right to rule from the gods, and thus based his rule on divine intervention. Obeying the pharaoh meant adhering to the will of the gods.
Egyptian Kingdoms

Ancient Egyptian history is divided into three major time periods, known as kingdoms. The Old Kingdom spanned from 2700 to 2200 B.C. (B.C.E.), the Middle Kingdom spanned from 2050 to 1652 B.C. (B.C.E.), and the New Kingdom spanned from 1567 to 1085 B.C. (B.C.E). In this interactivity, you will explore each of these kingdoms. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
Life in Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, men and women married in their early teens, and marriages were arranged by parents. Most marriages were monogamous, meaning they consisted of marriage to one person. If a woman could not bear children, a man was permitted to have more than one wife. Also, while men were considered the head of the household, women were responsible for educating their children and ensuring the home ran smoothly. Women were allowed to own property and receive inheritance. Some women even held positions as priestesses and business owners, although most offices were only open to men.Similar to many other early civilizations, Egypt's culture had a class system with the pharaoh and the royal family at the top. In this interactivity, you will discover details about each class. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
Ancient Egypt Review

 Now that you have explored ancient Egypt's geography, kingdoms, and class system, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.
Now that you have explored ancient Egypt's geography, kingdoms, and class system, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.
 Ancient Egyptian civilization was located in northeast Africa, and centered along the Nile River, the longest river in the world. Without the Nile River, Egypt would exist as a barren desert. Specifically, the Nile River stretched from Lake Victoria in the south, in what was called Upper Egypt; it flowed into the Nile River Delta in the north, in what was called Lower Egypt, and emptied into the Mediterranean Sea. In the image, notice how the Nile River Delta is triangular-shaped. It is actually marshland formed by deposits of fertile soil found at the mouth of the Nile River. Egyptians relied on the yearly flooding to produce nutrient-rich soil, which enabled them to grow crops and become prosperous. Fortunately, natural boundaries around ancient Egypt, like the Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, and a variety of deserts, served as barriers against threats from outside invaders.
Ancient Egyptian civilization was located in northeast Africa, and centered along the Nile River, the longest river in the world. Without the Nile River, Egypt would exist as a barren desert. Specifically, the Nile River stretched from Lake Victoria in the south, in what was called Upper Egypt; it flowed into the Nile River Delta in the north, in what was called Lower Egypt, and emptied into the Mediterranean Sea. In the image, notice how the Nile River Delta is triangular-shaped. It is actually marshland formed by deposits of fertile soil found at the mouth of the Nile River. Egyptians relied on the yearly flooding to produce nutrient-rich soil, which enabled them to grow crops and become prosperous. Fortunately, natural boundaries around ancient Egypt, like the Mediterranean Sea, Red Sea, and a variety of deserts, served as barriers against threats from outside invaders.



