Ancient India - The Aryan Civilization
India's Geography
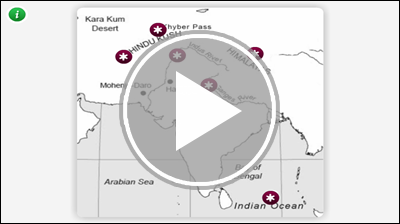
India is a large landmass called a subcontinent, or a sub-division of a continent. Because of India's physical features, the Indian civilization was well-protected from invaders. In this interactivity, you will learn more about the unique physical features of India. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
Mojenjo-Daro and Harappa

Structural remains of Mohenjo-Daro
While the ancient Egyptians were building pyramids, people in the Indus Valley were building India's first cities. Two of the largest cities that archaeologists have uncovered are Mojenjo-Daro and Harappa. The artifacts excavated from these sites reveal a highly sophisticated people. For example, each city was constructed on a grid system with the most important buildings in the center of the city, and a variety of "neighborhoods" in the surrounding area. Buildings were constructed from oven-baked bricks, all of which were equal in size and able to seal in water for public baths. These early cities also had a plumbing and sewage system.
Evidence suggests that around 1500 B.C. (B.C.E.), Mojenjo-Daro and Harappa were on the brink of collapse. Many historians attribute this collapse to conquests by nomadic people who entered the Indus Valley through the Khyber Pass of the Hindu Kush mountains. Who were these invaders, where did they originate, and how did they transform India? All of these questions will be answered as you continue through this topic.
Indo-Aryans, Mauryans, and Guptas

Eventually ancient Indian civilizations spread beyond the Indus River Valley, into the Ganges River Valley and the Indian subcontinent. Think back to the warm-up activity. Do you believe Damyanti Hingorani's displacement had similarities to those of people impacted by the spread of ancient Indian civilizations? Consider this as you explore three important groups of people in ancient India: Indo-Aryans, Mauryans, and Guptas. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
Ancient India Review

 Now that you have learned about Ancient India, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.
Now that you have learned about Ancient India, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.




