Module 7: Industrial Revolution and Its Impact
In this module, you will discover the major technological changes which sparked the Industrial Revolution in England and then spread throughout Europe. As a result of these changes, you will see how the labor force and working conditions changed for the working class.
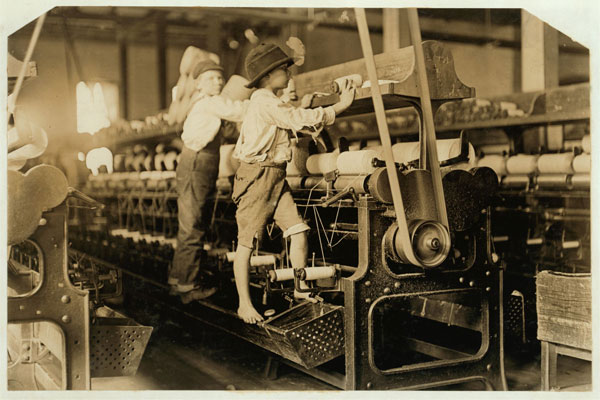 |
Child laborers in Macon, Georgia, 1909
Generally, working conditions deteriorated during the Industrial Revolution which led workers to create labor unions and go on strike. Other people created new economic theories like socialism and communism as a solution to these issues.
With so much focus on producing as many goods as possible, European countries looked once again to expand their territories in their search for raw materials. However, not all areas of the world welcomed the European powers and resisted through armed conflict as well as social and intellectual movements.
Pre-Assessment
Throughout this module, you will meet many great thinkers of the Industrial Revolution who wrote important philosophical treatises or invented new technologies. These trailblazers had a lasting impact on the world. In this non-graded interactivity, see how many of these people you are already familiar with. Click the player to begin.
Key Vocabulary
To view the definitions for these key vocabulary terms, visit the course glossary.
| Adam Smith | Enclosure Movement | Louis Pasteur |
| Boxer Rebellion | entrepreneur | missionary |
| capital | factory system | nationalism |
| capitalism | Friedrich Engels | proletariat |
| collective bargaining | Henry Bessemer | protectorate |
| colony | imperialism | raw materials |
| communism | Indian National Congress | socialism |
| cottage industry | Industrial Revolution | sphere of influence |
| East India Company | James Hargreaves | strike |
| economics | James Watt | suffrage |
| Edward Jenner | Karl Marx | urbanization |
| Eli Whitney | labor union |