Multiplying and Dividing Polynomials
Multiplying and Dividing Polynomials – Algebra Tiles
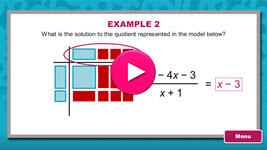 Algebra tiles provide you with the opportunity to use concrete objects to model and perform operations. In this interactivity, you will learn how to use algebra tiles to model and simplify products and quotients of polynomials. Click the player button to begin.
Algebra tiles provide you with the opportunity to use concrete objects to model and perform operations. In this interactivity, you will learn how to use algebra tiles to model and simplify products and quotients of polynomials. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
Finding Products of Polynomials
 In this interactivity, you will apply your knowledge of the distributive property and combining like terms to determine the products of polynomial expressions. Your knowledge of the properties of exponents will also be useful to you as work through this lesson. Click the player button to begin.
In this interactivity, you will apply your knowledge of the distributive property and combining like terms to determine the products of polynomial expressions. Your knowledge of the properties of exponents will also be useful to you as work through this lesson. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
FOIL
You have already learned how the distributive property allows you to multiply binomial expressions. The FOIL method is a strategy to help you remember how to apply the distributive property to find the product of binomial expressions. FOIL is an acronym that stands for:
First, Outer, Inner, Last
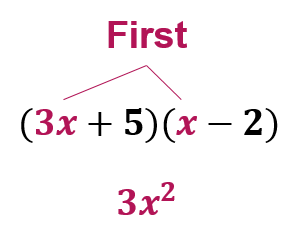
The example below demonstrates how to use the FOIL method to multiply binomials.
| (3x + 5)(x − 2) |
 |
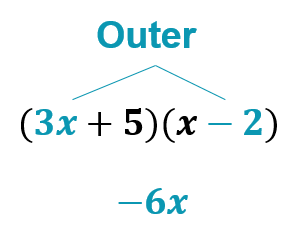 |
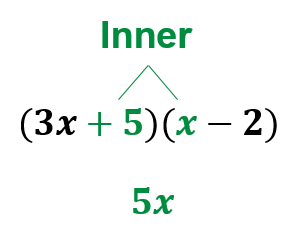 |
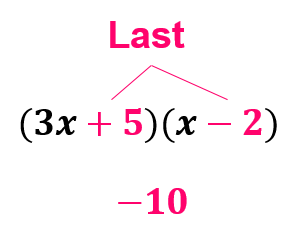 |
3x2 − 6x + 5x − 10 |
3x2 − x − 10 |
Special Products
There are patterns that arise when you find the product of certain binomial expressions. These products are referred to as special products. Read through the table below to learn more about special products.
| Special Product | Example | ||||||||||||||||||
| Perfect Square Trinomial | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Difference of Squares | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Practical Problem: Area of a Rectangle
Look at the example below to see how polynomials can be used to model a practical problem.
Example
Wendy has a rectangular-shaped garden. If the width of the garden is two feet more than four times its length, write an expression to represent the garden's area.
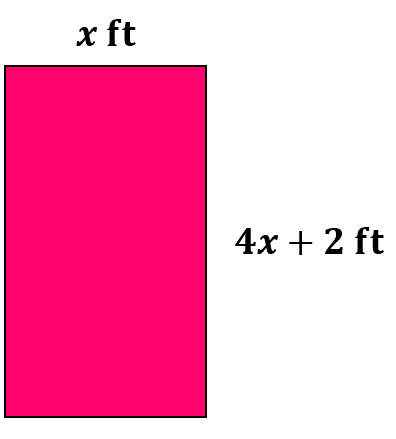
Area of a rectangle = length x width
| = | x(4x + 2) | ||
| = | 4x2 + 2x |
Dividing Polynomial Expressions
Take a moment to look at the example below to see how to use the Quotient of Powers Property to divide polynomial expressions.
Example
Simplify the following expression:
| −40x2 + 24x 8x |
|
−40x2 + 24x
8x |
= |
−40x2
8x |
+ | 24x 8x | Consider the expression as the sum of quotients. |
| = | −5x + 3 | Quotient of Powers of Property |
Multiplying and Dividing Polynomials Review
![]()
 Now that you have learned about multiplying and dividing polynomials, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.
Now that you have learned about multiplying and dividing polynomials, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.
![]() Did you answer the content review questions incorrectly? Do you want more instruction or extra practice? If so, view the videos Products of Binomials, Special Products, Modeling Products of Binomials, Products of a Binomial and a Trinomial, and Dividing Polynomials from eMediaVASM.
Did you answer the content review questions incorrectly? Do you want more instruction or extra practice? If so, view the videos Products of Binomials, Special Products, Modeling Products of Binomials, Products of a Binomial and a Trinomial, and Dividing Polynomials from eMediaVASM.