Solving Literal Equations
Properties of Real Numbers
The substitution property states that if two values are equal, one value can replace the other in an equation or inequality. In the table below, you will apply this property by substituting 2 for a, 3 for b, and 4 for c. This will allow you to investigate the properties of real numbers.
| Property | Addition | Multiplication |
| Associative Property | When adding, real numbers can be grouped together in any manner. a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c 2 + (3 + 4) = (2 + 3) + 4 2 + 7 = 5 + 4 9 = 9 |
When multiplying, real numbers can be grouped together in any manner. a · (b · c) = (a · b) · c 2 · (3 · 4) = (2 · 3)· 4 2 · 12 = 6 · 4 24 = 24 |
| Commutative Property | Real numbers can be added together in any order. a + b = b + a 2 + 3 = 3 + 2 5 = 5 |
Real numbers can be multiplied in any order. a · b = b · a 2 · 3 = 3 · 2 6 = 6 |
| Identity Property | Adding 0 to a real number does not change its value. a + 0 = a 2 + 0 = 2 The additive identity is 0. |
Multiplying a real number by 1 does not change its value. a · 1 = a 2 · 1 = 2 The multiplicative identity is 1. |
| Inverse Property | The sum of a real number and its opposite equals 0. a + (−a) = 0 2 + (−2) = 0 The additive inverse of a real number is its opposite. |
The product of a real number and its reciprocal equals 1. a ·
1a
= 1 2 ·
12
= 1The multiplicative inverse of a real number is its reciprocal. |
The Distributive Property
Apply the distributive property to find the product of a real number and a sum.
a (b + c) = ab + ac 2(3 + 4) = 2(3) + 2(4) 2(7) = 6 + 8 14 = 14 |
Properties of Equality
 The properties of equality guarantee that there are certain operations that you can perform to solve an equation. In this interactivity, you will explore some of these properties and learn how they are used to solve equations. Click the player button to begin.
The properties of equality guarantee that there are certain operations that you can perform to solve an equation. In this interactivity, you will explore some of these properties and learn how they are used to solve equations. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
More Properties of Equality
 In this interactivity, you will extend your knowledge of the properties of equality. You will investigate additional properties that allow you to perform the operations needed to solve equations. Click the player button to begin.
In this interactivity, you will extend your knowledge of the properties of equality. You will investigate additional properties that allow you to perform the operations needed to solve equations. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
Solving Literal Equations
 A literal equation is an equation that includes more than one variable. The variables are used to represent known and unknown values, such as in a formula. For example, the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle is p = 2l + 2w, where p represents the perimeter, l represents the rectangle’s length, and w represents the rectangle’s width. How could you write an equation that could be used to determine the width of the rectangle, if the length and perimeter are known? In this interactivity, you will learn how to apply the properties of equality to solve literal equations for specified variables. Click the player button to begin.
A literal equation is an equation that includes more than one variable. The variables are used to represent known and unknown values, such as in a formula. For example, the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle is p = 2l + 2w, where p represents the perimeter, l represents the rectangle’s length, and w represents the rectangle’s width. How could you write an equation that could be used to determine the width of the rectangle, if the length and perimeter are known? In this interactivity, you will learn how to apply the properties of equality to solve literal equations for specified variables. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity.
Solving Literal Equations Review
![]()
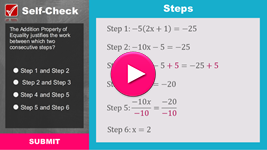 Now that you have explored how to solve literal equations, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.
Now that you have explored how to solve literal equations, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player button to get started.
![]() Did you answer the content review questions incorrectly? Do you want more instruction or extra practice? If so, view the videos Solving Literal Equations, Properties of Real Numbers, and Properties of Equality from eMediaVASM.
Did you answer the content review questions incorrectly? Do you want more instruction or extra practice? If so, view the videos Solving Literal Equations, Properties of Real Numbers, and Properties of Equality from eMediaVASM.