
The Celestial Sphere
 The sky around you is like a great dome. If you have ever visited a planetarium, you could see the dome before the lights go out. Stars are projected on the inside of the great dome to mimic the night sky. Why a dome? Because of the curvature of the Earth, the sky appears to curve as well. As the night progresses, this great dome seems to swirl around the Earth. This great dome is called the celestial sphere.
The sky around you is like a great dome. If you have ever visited a planetarium, you could see the dome before the lights go out. Stars are projected on the inside of the great dome to mimic the night sky. Why a dome? Because of the curvature of the Earth, the sky appears to curve as well. As the night progresses, this great dome seems to swirl around the Earth. This great dome is called the celestial sphere.
In ancient times, people believed that all of the stars were fixed on this great sphere and it spun around the Earth. They said that at times you could hear the great sphere of the Earth, the Moon, the Sun, planets, and stars grinding past one another. Today, we know that the stars are not all the same distances away from the Earth and that a great celestial sphere of stars does not exist. The model of a great celestial sphere, however, is still an excellent representation of how the sky appears and how it works.
 The celestial sphere is a useful tool. It appears as if the sky rotates around us. In reality, the motion is due to the Earth rotating and revolving. In this interactivity, click on each of the icons to learn more about the different parts of the celestial sphere. Click the player to begin.
The celestial sphere is a useful tool. It appears as if the sky rotates around us. In reality, the motion is due to the Earth rotating and revolving. In this interactivity, click on each of the icons to learn more about the different parts of the celestial sphere. Click the player to begin.
Azimuth and Altitude
If you are looking to find a constellation in the night sky, the celestial sphere would be helpful to study beforehand. How do you find the constellations in the night sky? Two coordinates can help any observer find an object in the sky.
 Altitude
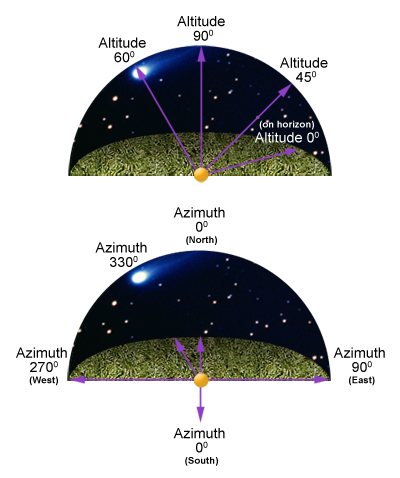
Altitude
Altitude is how high above the horizon the object of interest is. It is measured by the degree of the angle between the horizon, the observer (as indicated by the orange dot in the image), and the point of interest.
- Directly overhead is 90 degrees.
- On the horizon is 0 degrees.
Azimuth
Azimuth is the direction in which the observer is looking or where the point of interest lies -- north, south, east or west. These are the cardinal directions, and they are measured between 0 and 360 degrees.
- North is 0 degrees or 360 degrees.
- East is 90 degrees.
- South is 180 degrees.
- West is at 270 degrees.
If a star that you wish to view is at 330 degrees azimuth and 60 degrees altitude, as in the image shown, then you would look to the north-west about two-thirds of the way up the sky from the horizon.
Sidereal Day
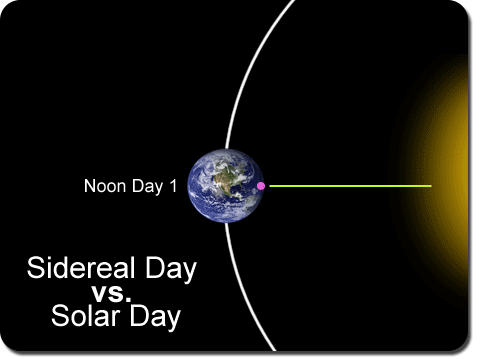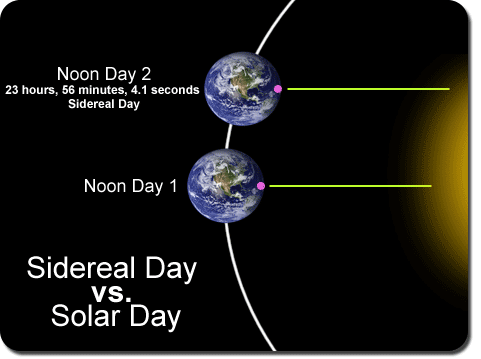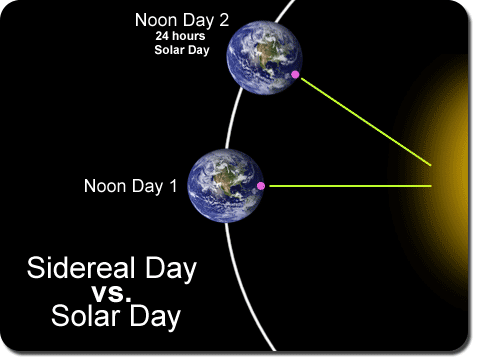 Astronomers use the sidereal day to determine the Earth’s location in its rotation relative to the stars instead of relative to the sun. It takes into account not only the Earth’s rotation, but also the fact that the Earth moves along in its orbit during the rotation. This makes the sun appear in a different location in the sky from day to day at the end of a rotation.
Astronomers use the sidereal day to determine the Earth’s location in its rotation relative to the stars instead of relative to the sun. It takes into account not only the Earth’s rotation, but also the fact that the Earth moves along in its orbit during the rotation. This makes the sun appear in a different location in the sky from day to day at the end of a rotation.
The sidereal day is the actual time it takes for the Earth to complete a single rotation on its axis, which makes the sidereal day actually twenty-three hours, fifty-six minutes, and 4.1 seconds. --- That is four minutes shorter than the twenty-four hours needed in a solar day that relies upon the sun returning to the same visual location from day to day. In other words, it takes almost four extra minutes in the solar day for the Earth to rotate a bit more to face the sun in the same visual location because of the Earth’s additional movement along the orbit.
If you watch the stars for multiple nights, you might realize that the stars come out four minutes earlier each night, but they come out at nearly the same location at the same sidereal time. Astronomers use the sidereal day to figure out where to point their telescopes in order to observe a certain star or other celestial body.
Do Stars Rise and Set?
![]() The rotation of the Earth gives the appearance from Earth that the stars rise and set. Some stars, however, do neither. Visit the University of Nebraska - Lincoln's Paths of the Stars website and learn about the rise and set stars, and the circumpolar and never-rise stars. Make sure to take notes on each type of star.
The rotation of the Earth gives the appearance from Earth that the stars rise and set. Some stars, however, do neither. Visit the University of Nebraska - Lincoln's Paths of the Stars website and learn about the rise and set stars, and the circumpolar and never-rise stars. Make sure to take notes on each type of star.
The Celestial Sphere Review

![]() Now that you have learned about the celestial sphere and the movement of stars, practice what you have learned in this non-graded activity. Read each statement and decide whether it is True or False. Then, select the appropriate answer and click SUBMIT to check your answer. Click the player to get started.
Now that you have learned about the celestial sphere and the movement of stars, practice what you have learned in this non-graded activity. Read each statement and decide whether it is True or False. Then, select the appropriate answer and click SUBMIT to check your answer. Click the player to get started.


