Meiosis
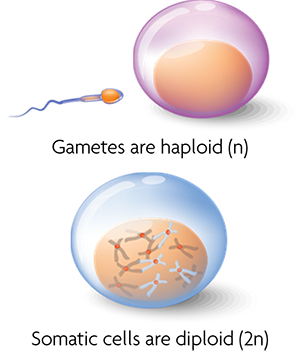 Unlike asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction requires two individuals, a male and a female, to produce new offspring. In humans, the male gamete is the sperm cell, and the female gamete is the egg cell. Each gamete contains a compliment of chromosomes, which is how the resulting offspring inherits traits from each parent. Reproduction occurs when the sex cells, or gametes, fuse to form a new organism.
Unlike asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction requires two individuals, a male and a female, to produce new offspring. In humans, the male gamete is the sperm cell, and the female gamete is the egg cell. Each gamete contains a compliment of chromosomes, which is how the resulting offspring inherits traits from each parent. Reproduction occurs when the sex cells, or gametes, fuse to form a new organism.
Body cells, or somatic cells, have a full set of chromosomes. Unlike somatic cells, gametes are used for sexual reproduction because they have half of the number of chromosomes that body cells have. There are 46 chromosomes in each human body cell. If a cell with 46 chromosomes fused with another cell that also has 46 chromosomes, the resulting organism would have 92 chromosomes. A human with 92 chromosomes would contain too much genetic information and would likely perish. With each generation, if body cells were used for reproduction, the number of chromosomes in the organisms would double. In order to maintain the number of chromosomes from generation to generation, organisms produce gametes.
Sex cells are produced through the process of meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes by half, and produces haploid gametes. Haploid, represented by n, describes a cell with half the number of chromosomes. When the gametes fuse, they create a diploid organism. The full set of chromosomes for humans is 46, twenty-three from each parent. The chromosomes from one parent pair up with the chromosomes from the other parent to form twenty-three pairs of homologous chromosomes. Diploid cells are represented by 2n.
![]() In the 19th century, scientists discovered that plants and animals reproduced sexually. However, scientists were still unclear how cells differentiated to from different types of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. View 1905- Meiosis from eMediaVASM to observe sexual reproduction at a cellular level. Pay close attention to the different phased in the process of meiosis.
In the 19th century, scientists discovered that plants and animals reproduced sexually. However, scientists were still unclear how cells differentiated to from different types of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. View 1905- Meiosis from eMediaVASM to observe sexual reproduction at a cellular level. Pay close attention to the different phased in the process of meiosis.
Phases of Meiosis
 Meiosis, much like mitosis, goes through the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. Only meiosis goes through these phases twice. The process of mitosis creates two diploid daughter cells from one diploid parent cell. The processes of meiosis I and meiosis II creates four haploid gametes from one diploid cell. In meiosis, DNA is copied once and divided twice. In this interactivity, learn about the phases of meiosis, a process that is essential for sexual reproduction. Click the player button to begin.
Meiosis, much like mitosis, goes through the phases of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. Only meiosis goes through these phases twice. The process of mitosis creates two diploid daughter cells from one diploid parent cell. The processes of meiosis I and meiosis II creates four haploid gametes from one diploid cell. In meiosis, DNA is copied once and divided twice. In this interactivity, learn about the phases of meiosis, a process that is essential for sexual reproduction. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of the interactivity.
Importance of Meiosis
 Meiosis is important not only because it maintains the number of chromosomes from generation to generation, but also because it provides variation in a species. Organisms that reproduce asexually produce offspring that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This is beneficial, as long as the environment in which the organisms live does not change.
Meiosis is important not only because it maintains the number of chromosomes from generation to generation, but also because it provides variation in a species. Organisms that reproduce asexually produce offspring that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This is beneficial, as long as the environment in which the organisms live does not change.
Consider however, what would happen if a disease were to be introduced to a field of genetically identical corn plants to which the corn have no immunity. The entire field would be wiped out. The same disease introduced to a field in which the plants were genetically diverse would not be as destructive. While some plants may be killed, other genetically different plants may survive to reproduce. Because of the genetic diversity the species was able to survive.
Meiosis Review
![]()
 Review your knowledge of meiosis in this non-graded activity. Complete each paragraph by dragging and dropping the correct word from the word bank into blank space provided. Click the player button to get started.
Review your knowledge of meiosis in this non-graded activity. Complete each paragraph by dragging and dropping the correct word from the word bank into blank space provided. Click the player button to get started.