
Measurement Systems
The International System of Units
 Measurements are a very important part of any science course you will take. In fact, they are an important part of your everyday life. Imagine going to the gas station and asking the attendant for “three.” Three gallons? Three dollars worth of gas? Three WHAT? Measurements represent quantity, called a magnitude; however, they also have a unit. Their measurement and the unit chosen is dependent on the quantity being measured. Scientists around the world use the International System of Units, also known as the SI system. There are many advantages to using the SI system:
Measurements are a very important part of any science course you will take. In fact, they are an important part of your everyday life. Imagine going to the gas station and asking the attendant for “three.” Three gallons? Three dollars worth of gas? Three WHAT? Measurements represent quantity, called a magnitude; however, they also have a unit. Their measurement and the unit chosen is dependent on the quantity being measured. Scientists around the world use the International System of Units, also known as the SI system. There are many advantages to using the SI system:
- In the SI system there is only one unit for each type of quantity. For instance, if you are measuring the mass of an object, you would always use grams.
- There are very few units in the SI system to worry about: only about 30. In the non-SI system there are thousands of different units.
- In the SI system, fractions or multiples of units are represented by simple, easy to pronounce prefixes like milli-, kilo- or giga-.
- SI units do not use fractions, they only use decimals. Consider this: have you ever tried to make a third of a recipe of cookies and you need to determine what 1/3 of 2/3 cup of sugar is?
- The SI system is based on units of ten. When making conversions between units, the decimal place just needs to be moved.
Basic SI Units of Measurement
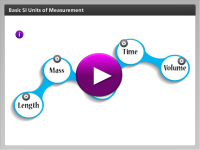 You may be used to measuring length in inches, feet, and miles, but how does measuring length change in the International System of Units (SI)? Each type of measurement has its own unit in the SI system. In this interactivity, click on each of the spinning icons to learn more about the most important units of measurement you will use in chemistry.
You may be used to measuring length in inches, feet, and miles, but how does measuring length change in the International System of Units (SI)? Each type of measurement has its own unit in the SI system. In this interactivity, click on each of the spinning icons to learn more about the most important units of measurement you will use in chemistry.
Download a printable version of the interactivity.
Unit Prefixes
Prefixes are added to the base units to represent a larger or smaller quantity. The table below shows the major prefixes used in the SI system. Based on the prefixes, a millimeter would represent 1/1000th of a meter, while a kilometer would equal one thousand meters. The metric system may seem confusing at first, but it is actually very easy to use because it is based on the number ten. For example, there are ten millimeters in one centimeter, one hundred centimeters in one meter, and one thousand meters in one kilometer.
Prefix |
Symbol |
Meaning |
Examples |
| kilo- | k | 1000 times the base unit | 0.001 kilometer 0.001 kiloliter 0.001 kilogram |
| hecto- | h | 100 times the base unit | 0.01 hectometer 0.01 hectoliter 0.01 hectogram |
| deka- | da | 10 times the base unit | 0.1 dekameter 0.1 dekaliter 0.1 dekagram |
| meter liter gram |
m l g |
the base unit | 1 meter 1 liter 1 gram |
| deci- | d | 1/10 of the base unit | 10 decimeters 10 deciliters 10 decigrams |
| centi- | c | 1/100 of the base unit | 100 centimetes 100 centiliters 100 centigrams |
| milli- | m | 1/1000 of the base unit | 1000 millimeters 1000 milliliters 1000 milligrams |
The SI system may seem confusing at first, but it is actually very easy to use because it is based on the number 10. For example, there are 10 millimeters in 1 centimeter, 100 centimeters in 1 meter, and 1000 meters in 1 kilometer. Are you still not so sure? Converting numbers between units only involves moving the decimal place. Look at the chart above. The smallest unit has the prefix milli- and the largest unit prefix is kilo-. To convert between units, you simply need to move the decimal point. If you are converting to a smaller unit of measurement, move the decimal to the right one space for each prefix. If you are converting to a larger unit of measurement, move the decimal to the left one space for each prefix.
Example 1:
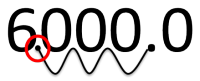 If you wanted to convert 6000.0 meters to kilometers, you would have to move the decimal point over three places to the left. If you have converted this correctly, you will find that there are 6.0 kilometers found in 6000.0 meters.
If you wanted to convert 6000.0 meters to kilometers, you would have to move the decimal point over three places to the left. If you have converted this correctly, you will find that there are 6.0 kilometers found in 6000.0 meters.
Example 2:
 How many centigrams exist in 3.0 grams of salt? Hint: This time you have to move the decimal point to the right. If you have converted this correctly, you will find that there are 300.0 centigrams in 3.0 grams of salt.
How many centigrams exist in 3.0 grams of salt? Hint: This time you have to move the decimal point to the right. If you have converted this correctly, you will find that there are 300.0 centigrams in 3.0 grams of salt.
SI Units Conversion Review

![]() Practice your ability to convert measurements using the SI system in this non-graded activity. Read the directions associated with each question and provide the correct answer or answers. Then, click SUBMIT to check your response. Click the interactivity thumbnail and then click NEXT to get started.
Practice your ability to convert measurements using the SI system in this non-graded activity. Read the directions associated with each question and provide the correct answer or answers. Then, click SUBMIT to check your response. Click the interactivity thumbnail and then click NEXT to get started.
Accuracy and Precision in Measurement
 Now that you have explored the SI system of measurement, examine how to correctly record measurements. View this presentation to explore precision and accuracy in measurement using certain and uncertain digits, as well as how to determine the average or mean of a set of measurements.
Now that you have explored the SI system of measurement, examine how to correctly record measurements. View this presentation to explore precision and accuracy in measurement using certain and uncertain digits, as well as how to determine the average or mean of a set of measurements.
View a printable version of the interactivity.


