
Net Ionic Equations and Spectator Ions
Being able to properly write net ionic equations relies on your ability to write and balance a chemical reaction, while identifying the spectator ions. A spectator in sports is an audience member who does not participate in the sporting event, but watches the event as an observer. Spectator ions serve a similar role. These ions do not participate in the reaction; instead, they are present as both a reactant and a product. You could say that they “look on” from the sidelines. Once the spectator ions are identified in a reaction, they are left out of the net ionic equation.
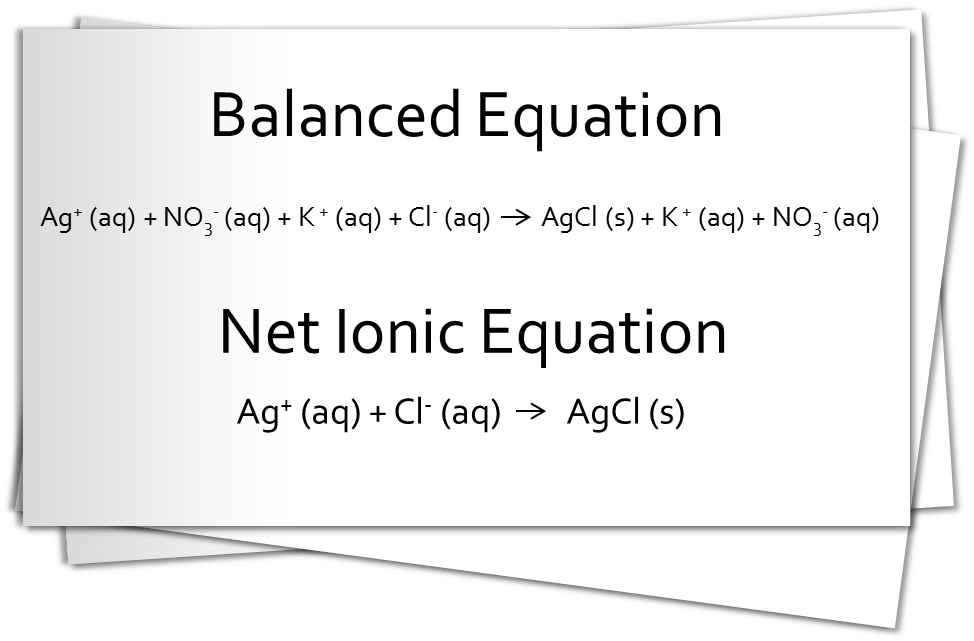
Take a moment to review the reaction between an aqueous solution of silver nitrate and an aqueous solution of potassium chloride, as shown in the image above. As you can see from the equations, when these solutions are mixed, insoluble AgCl precipitates. The ions K+ and NO3- remain in solution. K+ and NO3- are the spectator ions. They do not participate in the reaction and are removed from the net ionic equation.
Steps for Writing and Balancing Net Ionic Equations
 Writing and balancing a net ionic equation requires that you follow four steps. Next, you will learn how to write a balanced, net ionic equation for the reaction of aqueous solutions of BaCl2 and Na2SO4. In this activity, click NEXT to examine each step in the strategy used for balancing net ionic equations.
Writing and balancing a net ionic equation requires that you follow four steps. Next, you will learn how to write a balanced, net ionic equation for the reaction of aqueous solutions of BaCl2 and Na2SO4. In this activity, click NEXT to examine each step in the strategy used for balancing net ionic equations.
View a printable version of the interactivity.
Net Ionic Equations Review
![]()
 Now that you have explored how to write and balance net ionic equations, complete this activity to test your knowledge. In this non-graded activity, read each question and complete the net ionic equations for each of the chemical reactions. Drag and drop the correct balanced net ionic equation in the blank space provided. To check your response click SUBMIT. Click on the interactivity thumbnail, and then click NEXT to get started.
Now that you have explored how to write and balance net ionic equations, complete this activity to test your knowledge. In this non-graded activity, read each question and complete the net ionic equations for each of the chemical reactions. Drag and drop the correct balanced net ionic equation in the blank space provided. To check your response click SUBMIT. Click on the interactivity thumbnail, and then click NEXT to get started.


