Charles’ Law, Boyle’s Law, Avogadro’s Principle, Gay-Lussac’s Law, and the Combined Gas Law

![]() Before you begin the scientific investigation below, make sure to download the Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report. As you complete this scientific investigation, fill in any needed information on the report template. If you need more information about each section of the report, please visit the Developmental Module.
Before you begin the scientific investigation below, make sure to download the Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report. As you complete this scientific investigation, fill in any needed information on the report template. If you need more information about each section of the report, please visit the Developmental Module.
This scientific investigation is available below or in a printable version.
Introduction
Different gas laws describe the different properties that a gas exhibits. You have learned about four gas laws. Charles’s Law tells chemists that the temperature of a gas is related to its volume. Boyle’s Law is observed when pressure is modified. Once pressure is decreased by half, the volume will decrease by half of the original amount. Avogadro’s Law states that doubling the number of moles doubles the gases volume. Lastly, the Gay-Lussac’s Law gives the relationship between pressure and temperature.
Objectives
In this scientific investigation, you will:
- predict how changing a variable such as pressure, temperature, and volume influences other gas properties; and
- predict how the number of gas molecules affects the behavior of a gas.
Hypothesis
Using the Procedure and Data Collection section below, read through the procedural information for this scientific investigation. Based on your understanding of the procedure, develop your own hypotheses which describe the expected results. You should consider the following questions: How do pressure, temperature, and volume impact the behavior of a gas? How do the number of gas molecules influence the behavior of a gas? Record these hypotheses in the Hypothesis section of your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report.
Gas Properties Simulation
(click on image below to access simulation)
Provided by:
PhET Interactive Simulations
University of Colorado
http://phet.colorado.edu
Procedure and Data Collection
Simulation Set-Up (see image at the right)
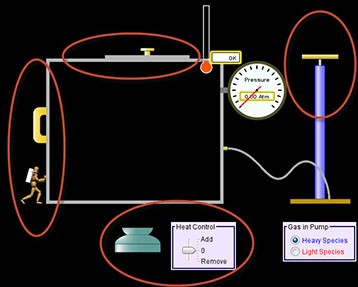 Open the Gas Properties simulation.
Open the Gas Properties simulation.- Take a few moments to become familiar with the simulator. Pump the handle, add heat, and change the size of the box by click on the different controls. View the image to the right to see where each of these controls are located. Once you are done experimenting with the simulation, click Reset to reset the simulation.
Part I: Constant Temperature
- Using the toolbar on the right side of the simulation, keep the temperature constant by selecting Temperature. In the radio buttons under Gas in Pump, make sure that Heavy Species is selected.
- Click measurement tools and select stopwatch.
- Grab the handle of the pump and give it one full pump. Quickly start the stopwatch. Wait thirty seconds and click stop on the stopwatch. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Temperature Data Table in the Step 3 row.
- Without resetting the simulation, open the lid by sliding it to the left. Start the stopwatch and let it run for one minute. Stop the stopwatch. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Temperature Data Table in the Step 4 row.
- Without resetting the simulation, use the handle on the wall to push the wall to the right so that it aligns under the lid handle. Start the stopwatch and let it run for thirty seconds. Stop the stopwatch. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Temperature Data Table in the Step 5 row.
- Without resetting the simulation, grab the handle of the pump and give it two full pumps. Start the stopwatch and let it run for thirty seconds. Stop the stopwatch. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Temperature Data Table in the Step 6 row.
- Click Reset to reset the simulation.
Part II: Constant Pressure
- Using the toolbar on the right side of the simulation, keep the pressure constant by selecting Pressure.
- Grab the handle of the pump and give it one pump. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Pressure Data Table in the Step 2 row immediately. Let the simulation run for thirty seconds, and click Stop on the stopwatch. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Pressure Data Table in the Step 2 row.
- Using the handle on the wall, push the wall to the right back to its original position. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Pressure Data Table in the Step 3 row.
- Click Reset to reset the simulation.
Part III: Constant Volume
- Using the toolbar on the right side of the simulation, keep the volume constant by selecting Volume.
- Grab the handle of the pump and give it one full pump. Quickly start the stopwatch. Wait thirty seconds and click stop on the stopwatch. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Volume Data Table in the Step 2 row.
- Pump the handle twice to inject more gas into the chamber. Quickly start the stopwatch. Wait thirty seconds and click stop on the stopwatch. On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, record the pressure in atm, the temperature in Kelvin, and your observations in the Constant Volume Data Table in the Step 3 row.
Data
Use the data tables provided on your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report to record your data from this scientific investigation. The data tables are also shown below.
Constant Temperature Data Table
| Step | Pressure (atm) | Temperature (K) | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 3 | |||
| Step 4 | |||
| Step 5 | |||
| Step 6 |
Constant Pressure
| Step | Time | Pressure (atm) | Temperature (K) | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 2 | 0 seconds | |||
| 30 seconds | ||||
| Step 3 |
Constant Volume
| Step | Pressure (atm) | Temperature (K) | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 2 | |||
| Step 3 |
Data Analysis
In the Data Analysis section of your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, provide the responses to the following questions:
Constant Temperature
- What does the pump control in this experiment?
- What does the handle on the wall control in this experiment?
- What purpose does the lid serve in this experiment?
- Why did the lid blow off in step four when the temperature was held constant?
Constant Pressure
- Why did the wall move towards the left when gas entered the chamber?
- What happened when you used the handle to reset the volume of the chamber to its original size?
- What two variables changed in this experiment and why did those variables change?
Constant Volume
- Why did pressure build when you added gas to the chamber?
- How could you get the pressure to build to above 2 atm?
- How could you get the pressure to go below 1 atm?
Conclusion
Using the Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, compose three to four sentences describing an overall conclusion about the relationship between temperature, volume, and pressure. Base your conclusions on your data. Were your hypotheses true or false, how do you know? Use the data and notes that you collected from your simulation experience to form your conclusion. Make sure that your include information that your gained from data analysis to support your conclusion.
Experimental Sources of Error
On your Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, provide responses to the following questions: Are there any sources of error? If so, what are they, and what could be done to minimize error?
![]() Once you have completed the Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, please submit your work to the dropbox.
Once you have completed the Gas Properties Scientific Investigation Report, please submit your work to the dropbox.