Physical Geography of Sub-Saharan Africa
Physical Features of Sub-Saharan Africa

The African continent is on a high plateau. It is bordered by a narrow coastal plain and steep cliffs called escarpments. Unlike North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa contains a wide variety of landforms and physical features. In this interactivity, you will explore the unique physical geography of Sub-Saharan Africa. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Climate Regions
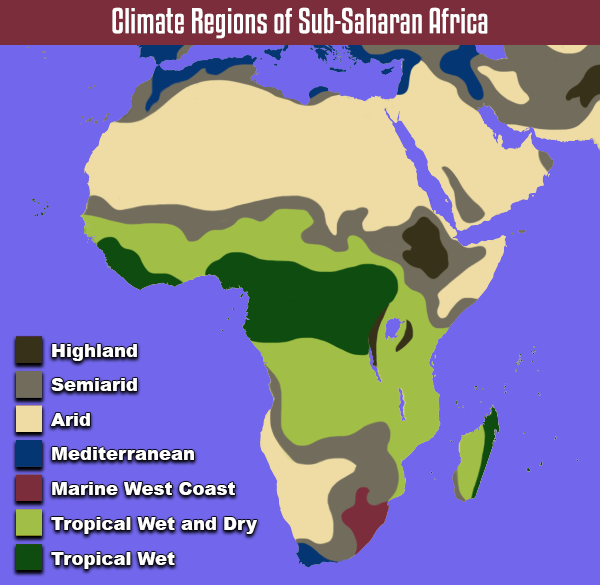
Africa has a symmetrical climate zone pattern. The equator is located in the middle of the region. There is a similar pattern of climate zones as you move north and south of the equator. There is a tropical wet climate zone located near the equator. This climate zone is characterized by warm temperatures, plentiful rainfall, and rainforest vegetation. The world’s second-largest area of rainforest is located in this region.

Tropical wet and dry climate region in Kenya
North and south of the equator, the climate shifts to tropical wet and dry climate zones. A tropical wet and dry climate is warm year-round, but the amount of precipitation varies. There is usually a long dry season and a short rainy season. Savanna vegetation is commonly found in this type of climate. Savanna is characterized by thick tropical grassland with scattered trees.
As you continue to travel north and south, the climate shifts to semiarid and then to arid. In the north, the arid climate encompasses the Sahara. In the south, the arid climate encompasses the Kalahari and Namib Deserts. There are a few highland regions located in East Africa, near the Red Sea and the Great Rift Valley. Mediterranean and marine west coast climates can also be found in Southern Africa near the coast.
National Parks and Nature Reserves
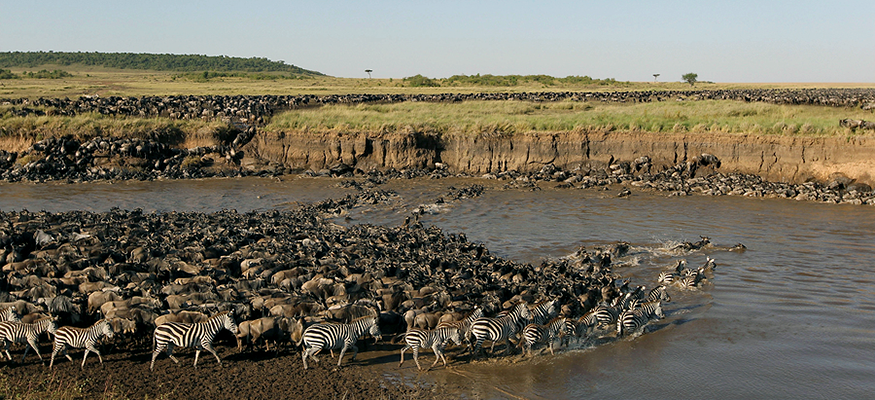

Wildebeest migration in Serengeti National Park, Tanzania
Africa is the second-largest continent in the world. This huge continent contains diverse physical geography. It is also home to many different species of plant and animal. African governments have established nature reserves and national parks throughout the region. These parks help preserve natural environments and endangered species. They also attract tourists from around the world.

Bwindi Impenetrable National Park in Uganda
Kilimanjaro National Park protects the area around Africa’s highest mountain, Mount Kilimanjaro. Bwindi Impenetrable National Park preserves a dense rainforest inhabited by endangered mountain gorillas and other species. Serengeti National Park is one of the most well-known nature reserves in Africa. It is located in Tanzania, near Lake Victoria, and includes more than 5,700 square miles of savanna. Serengeti National Park is home to a variety of animals, including lions, leopards, rhinoceros, elephants, giraffes, and zebras. These national parks are a few examples of many nature reserves found across Sub-Saharan Africa.
Physical Geography of Sub-Saharan Africa Review
![]() Now that you have learned about the major physical regions, landforms, and water features of Sub-Saharan Africa, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.
Now that you have learned about the major physical regions, landforms, and water features of Sub-Saharan Africa, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.
