The Immune System
Types of Immunity
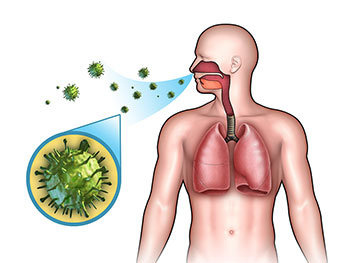 The immune system helps your body maintain homeostasis by preventing pathogens from disrupting your body's normal functions. A pathogen, commonly referred to as a "germ", is a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause illness. The body's resistance to a particular pathogen is called immunity. Humans have three types of immunity: innate, passive, and adaptive.
The immune system helps your body maintain homeostasis by preventing pathogens from disrupting your body's normal functions. A pathogen, commonly referred to as a "germ", is a bacterium, virus, or other microorganism that can cause illness. The body's resistance to a particular pathogen is called immunity. Humans have three types of immunity: innate, passive, and adaptive.
You are born with a natural type of protection, known as innate immunity, which protects you against pathogens that affect other species. Your skin and the mucous membranes of your nose, mouth, throat, and digestive tract are also part of your innate immunity. The skin is a protective, waterproof layer that prevents pathogens and materials from entering your body. Your skin secretes sweat, creating an acidic environment that destroys invaders. Mucus in your mouth, nose, and throat also trap pathogens in the air that you breathe. You acquired passive immunity from your mother before birth and afterwards if you were fed breastmilk. Passive immunity provided you with temporary protection until your own immune system strengthened. Adaptive immunity develops throughout your life as you are exposed to pathogens. Adaptive immunity is also developed through vaccinations.
The Immune Response
 As you already know, your immune system defends your body against disease. When a pathogen enters your body, it triggers your immune system to take action through a series of steps called the immune response. In this interactivity, you will learn more about the immune and lymphatic systems and how they work together to carry out the immune response. Click the player button to begin.
As you already know, your immune system defends your body against disease. When a pathogen enters your body, it triggers your immune system to take action through a series of steps called the immune response. In this interactivity, you will learn more about the immune and lymphatic systems and how they work together to carry out the immune response. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of the interactivity.
Allergies
 An allergy is when your immune system overreacts to a substance that is harmless to someone else. When the substance, called an allergen, enters your body, your immune system releases chemicals called histamines to defend against it. These histamines cause an allergic reaction, such as sniffling, sneezing, itching, and/or swelling. Antihistamines are used in allergy medications to counteract the histamines and can be lifesaving if the allergic reaction is so overactive that it restricts breathing.
An allergy is when your immune system overreacts to a substance that is harmless to someone else. When the substance, called an allergen, enters your body, your immune system releases chemicals called histamines to defend against it. These histamines cause an allergic reaction, such as sniffling, sneezing, itching, and/or swelling. Antihistamines are used in allergy medications to counteract the histamines and can be lifesaving if the allergic reaction is so overactive that it restricts breathing.
The Immune System Review
![]()
 Review your knowledge of the immune system in this non-graded activity. Read each question and select the correct response. Click the player button to get started.
Review your knowledge of the immune system in this non-graded activity. Read each question and select the correct response. Click the player button to get started.