
Acceleration
 Now that you have spent some time practicing acceleration calculations and acceleration on motion graphs, demonstrate your knowledge by correctly answering the following questions. Be sure to completely answer each question and to show all of your work.
Now that you have spent some time practicing acceleration calculations and acceleration on motion graphs, demonstrate your knowledge by correctly answering the following questions. Be sure to completely answer each question and to show all of your work.
This activity is available below or in a printable version.
Part I: Acceleration Calculations
- A roller coaster car uniformly picks up speed as it rolls down a slope. As it starts down the slope, its speed is 4 m/s. However, three seconds later, at the bottom of the slope, its speed is 22 m/s. What is its acceleration?
- A cyclist accelerates from 0 m/s to 8 m/s in 3 seconds. What is his acceleration? Is this acceleration higher than that of a car that accelerates from 0 to 30 m/s in 8 seconds?
- A car advertisement states that a certain car can accelerate from rest to 70 km/h in 7 seconds. Find the car’s acceleration in units of m/s.
- A lizard accelerates from 2 m/s to 10 m/s in 4 seconds. What is the lizard’s average acceleration?
- If a sports car with an initial velocity of 10 m/s, accelerates at a rate of 7 m/s2 for 3 seconds, what will be its final velocity?
- A speedboat initially moving at 15 m/s slows down to a stop with an acceleration of -1.5 m/s2. How much time passes during this change in velocity?
- In order to catch a speeding motorist, a police officer must accelerate to +35 m/s. The police office accelerates at a rate of +2.5 m/s for 8.0 seconds to reach this velocity. What was the officer's initial velocity?
Part II: Acceleration On Motion Graphs
For each of the graphs shown below, pick the label for the vertical axis that would make it match the given description.
 Standing Still
Standing Still- Position
- Velocity
- Acceleration
 Negative Acceleration
Negative Acceleration
- Position
- Velocity
- Acceleration
 Constant Negative Velocity
Constant Negative Velocity
- Position
- Velocity
- Acceleration
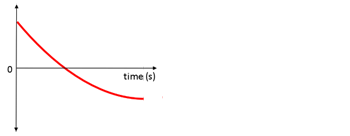 Positive Acceleration
Positive Acceleration
- Position
- Velocity
- Acceleration
 Constant Positive Velocity
Constant Positive Velocity
- Position
- Velocity
- Acceleration
 Negative Velocity
Negative Velocity
- Position
- Velocity
- Acceleration
![]()
Once you have finished answering the questions, submit your responses to the dropbox.



