Sound
Answer the following questions. Be sure to show all your work. This activity is available below or in a printable version.
Multiple choice. Indicate the best answer.
1. What type of wave is sound?
a. Surface wave
b. Longitudinal wave
c. Transverse wave
d. Tidal wave
2. How many beats per second will you hear when listening to sounds of 512 Hz and 515 Hz at the same time?
a. 2
b. 3
c. 5
d. 513.5
3. A singer breaking a glass with her voice is an example of:
a. Diffraction
b. Beats
c. Resonance
d. Amplitude
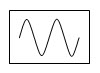
4. Which of the below sounds would be quieter and a lower pitch than the sound below to the right?
a.
b.
c.
d.
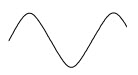
5. The picture to the right represents the fundamental frequency of a musical instrument. Which of the following would NOT represent a harmonic wave of this fundamental frequency?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
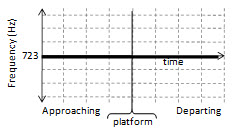
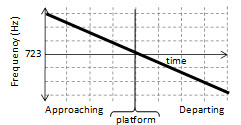
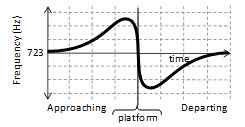
6. You are standing on a train platform as a train approaches at a 60 m/s. The train whistle emits a sound with a frequency of 723 Hz. Which of the following graphs best represents the frequency of the sound you hear as the train approaches, passes and then departs the platform without changing speed?
a.
b.
c.
d.
7. In order for a fighter jet to create a sonic boom, the jet must be traveling ___________ the speed of sound.
a. slower than
b. precisely at
c. quicker than
Matching.
8. Match the term on the left with the definition on the right, by writing the letter for the definition in the space provided to the right of each term.
Beats |
|
a. A longitudinal wave of pressure in air. |
Doppler Effect |
|
b. When oscillations match an objects natural frequency |
Harmonics |
|
c. An oscillation in the volume of sound that occurs when two similar frequencies are heard at the same time. |
Loudness |
|
d. The perceived musical note heard by a listener. Related to frequency of sound wave. |
Natural Frequency |
|
e. The perceived intensity of sound. Related to the amplitude of the sound wave. |
Pitch |
|
f. The higher frequencies that create standing waves for the same conditions (same string or same column of air). |
Resonance |
|
g. When an object moves faster than the speed of sound and the combined energies from multiple waves reaches an observer all at once, resulting in a great change in pressure |
Sonic Boom |
|
h. The lowest frequency at which an object will vibrate when disturbed. This is a function of the material, size and structure of the object. |
Sound |
|
i. When the perceived frequency of a waves is different from the frequency of the source because of relative motion between the observer and the source. |
Long Answer. Answer the following questions, showing all work.
9. An observer can hear a higher or a lower frequency than the actual frequency of a source because of the Doppler Effect. Describe the conditions necessary for the Doppler effect and provide one real example where you might expect to hear the Doppler effect.
![]()
Once you have finished answering the questions, submit your responses to the dropbox.