Northern and Central Europe
Northern Europe

There are ten countries that form the region of Northern Europe. These include the United Kingdom, Ireland, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and Iceland. In this interactivity, you will learn about each of these countries. As you explore Northern Europe, think about how the countries in this region are similar and how they are different. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Central Europe and the Low Countries

Central Europe is a region that includes the countries of France, Germany, Switzerland, and Austria. The Low Countries are a region defined by low elevation, including the countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. In this interactivity, you will explore Central Europe and the Low Countries. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
Cultural Influences of Northern and Central Europe

European culture is deeply rooted in history. The continent is home to many ethnic groups with different languages, cultures, and religions. Through conflict and cooperation, these groups have shaped the cultural landscape of Europe. In this interactivity, you will focus on the cultural influences of Northern Europe, Central Europe, and the Low Countries. Click the player to begin.
View a printable version of this interactivity or an ADA compliant transcript.
European Union

European Union flags in Brussels, Belgium
The European Union (EU) is Europe’s most important economic organization. It promotes development within its member countries through economic interdependence and cooperation. The EU was established in 1993 with six founding member nations. There are currently twenty-eight member nations; however, the UK is scheduled to leave the organization in 2019. Member countries benefit in the following ways:
- They pay no tariff when trading with one another;
- Citizens can live and work in any EU membership country;
- Companies can sell goods, build factories, and employ workers in any EU country; and
- Trade among the countries increases the standard of living.
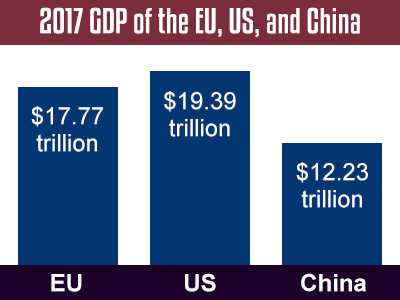
Collectively, the EU is one of the world’s leading economic powers. The gross domestic product (GDP) of the EU is similar to that of the United States and China. It is also one of the world’s largest importers and exporters.
There is debate over whether to add more member nations to the EU. Some oppose expansion. Others believe that preventing it will create two classes of states: the haves and the have-nots. As the EU grows and member nations become more interdependent, it has the potential of becoming a “super state” that plays a dominant role in world economics and politics.
Economic Characteristics of Northern and Central Europe

Paris, France
Most European nations are industrial and technological societies. This is especially true of nations found in Northern Europe, Central Europe, and the Low Countries. Countries in this region have highly developed economies and well-educated work forces. They also have some of the world’s highest standards of living. The majority of Europeans live in densely populated cities. As a result, Europe is one of the most densely populated areas on Earth.
Europe has an abundance of natural resources. These resources have helped shape the economies and cultures of the region. The North European Plain offers large areas of fertile soil. European farms use advanced techniques and technologies to produce high crop yields. The Danube and Rhine Rivers provide fresh water, but are also used for transportation. The Alps and other European mountain ranges contain mineral resources. Additionally, they serve as popular tourist attractions. Multiple countries operate offshore oil rigs in the North Sea, which contains oil reserves.

Dam in the Netherlands
Much of Europe has access to capital resources like technology and well-developed infrastructure. The Rhine-Main-Danube Canal system connects two major European rivers. This allows transportation and trade from the North Sea to the Black Sea. The Channel Tunnel, or Chunnel, is an undersea rail tunnel that crosses the English Channel. It provides quick transportation for people, vehicles, and cargo traveling between the UK and France. The Netherlands has a complex system of dams, dikes, and pumps. These have been used to reclaim land from the North Sea and prevent flooding.
European industry and urbanization have created environmental challenges. Air pollution and overcrowding impact Europe's largest cities. Water pollution threatens several rivers, particularly those used for transportation and trade. There have also been multiple oil spills in the North Sea.
Northern and Central Europe Review

 Now that you have learned about the major regions, cultural influences, and economic characteristics of Northern and Central Europe, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.
Now that you have learned about the major regions, cultural influences, and economic characteristics of Northern and Central Europe, review your knowledge in this interactivity. Click the player to get started.