
Challenges in a Contemporary World
Migration
The modern world is interconnected in so many ways, but one of the most striking is the way that people can easily travel vast distances in short amounts of time. Hop on a plane in New York, and in about thirteen hours, you could be in Beijing, China. While most people think of travel or movement for vacationing or work, many people travel to other countries for very different reasons, such as to escape conflicts, or to search for employment.
A refugee is someone who flees their home and/or country in order to escape danger or persecution. There are many reasons that a person might become a refugee including war, persecution of an ethnic group, or an environmental disaster, such as a flood or famine. When people become refugees on a large scale, this can cause a number of problems. Often, these refugees end up living in camps which are almost entirely dependent on support from governments or aid agencies in order to survive. Some of these camps become permanent homes for people who cannot, or will not, return to their homes. Over time, this can lead to resentment or the persecution of refugees by people in the countries to which they fled.
Migration in Europe
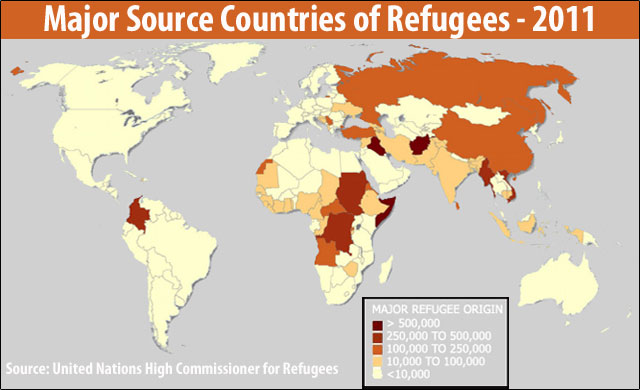
Economic migration is a story familiar to Americans because many people in the United States have family histories that involve immigration to this country. The United States is not unique in this pattern; these same circumstances are present in Europe.
In Europe, guest worker programs started in the mid-19th century. After several countries signed agreements, many immigrants traveled across country lines as guest workers, or foreign nationals who come to work with the approval of the local government. Even after many years in Europe, some of these immigrants remain abroad as guest workers with no path to citizenship. They often perform jobs that provide low wages or are considered undesirable by native citizens. Most European countries have declining birth rates and need the influx of non-native workers to keep their economies strong.
As immigrants arrive to a new country, they bring with them customs and behaviors from their place of origin. In some parts of Europe, the influx of people and different customs has caused tension and contributed to prejudice against these groups. European societies tend to be less diverse than the United States. As a result, immigrants may have a more difficult time integrating into the community.
Modern Ethnic and Religious Conflicts

Religion and ethnicity fuel much of the conflict in the world today. As a result of these differences, there are a number of regions with long-running conflicts between people living in the same country, as well as conflicts between people in different countries. View this presentation to explore some of the religious and ethnic conflicts in the modern world.
Download a printable version of the interactivity.
Impact of New Technologies
The year 2011 may best be remembered because Internet access and social networking sites fueled the Arab revolutions that brought down the leaders of three countries: Egypt, Tunisia, and Libya. The ability of protestors to use social media to transmit messages instantaneously both to people inside the country, as well as the outside world, was a crucial part of the success of these movements. Despite the best attempts of the countries' leaders, they were unable to address the grievances of the protestors. Although the downfall of Libya required the military intervention of the United States and NATO, both Egypt and Tunisia experienced non-violent revolutions.
Courtesy Kozuch.
As the map provided in this topic’s warm-up shows, access to these technologies is uneven throughout the world. With a population of almost 1.3 billion people, China has the largest Internet population on Earth, but there are government restrictions placed on the use of instantaneous communications tools to limit the use of the Internet to protest government policies. Other parts of the world, such as Africa, have limited access to computers in general. This means many technological advances in science and medicine bypass people living in the poorer, less-connected regions of the world.
Finally, some advanced technologies have created ethical issues. Some scientists have questioned whether genetically engineered crops that are resistant to disease and insects are safe for human consumption. The application of genetic engineering to mammals has ethical and religious implications. Scientists have the ability to clone animals, leading some to speculate they will one day be able to clone humans. Many people worry that this may start a movement towards trying to eliminate genetic "impurities" in the quest of perfection. This recalls the pursuit of the master race by certain people in the Nazi party. As scientists develop new methods of performing research and curing illness, for example using stem cells, the benefits that these provide will have to be balanced against what society sees as the ethical standards that need to be respected. This will certainly continue to be an issue for the foreseeable future.
Modern Ethnic and Religious Conflicts Review
Now that you have explored various challenges and conflicts in today's world, practice what you have learned in this interactivity. Read each question and select the most appropriate answer. Click the player to get started.


