
Cultural and Technological Changes of the Enlightenment

The Death of Socrates by Jacques-Louis David
European art and music changed greatly during the Enlightenment. The Enlightenment brought a new emphasis on order and balance to the fine arts and artists borrowed heavily from the styles and subjects of classical Greece and Rome. Paintings depicted classical subjects, public events, natural scenes, and living people as portraits. Often, the artists personified ideas in their works. For example, they painted liberty as a woman, or they represented justice as a woman holding scales.
In the area of music, the Baroque period lasted roughly from the early 1600s until 1750. Music from the Baroque period followed the music of the Renaissance and preceded the music of the Classical period. Baroque music was very complex and ornate. Baroque musicians introduced many of the musical concepts that are in use today. The Classical period of music then lasted from about 1750 until 1830. Like the painters of this time, composers were also heavily influenced by classical forms, which emphasized order, hierarchy, and clearer divisions within the music. Many of the best known music was written during this era by composers such as Ludwig van Beethoven and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. The symphony, as a musical form, was developed, as well as the modern symphonic instrumentation.
Concurrent with an increase in the use of reading materials, writers developed new styles of writing during the Enlightenment. Some of these styles are still in use today. A book written during this time, Don Quixote, is considered by many to be the first example of the modern novel.
Enlightenment Artists, Musicians, Philosophers, and Writers
In this interactivity, explore the artists, musicians, and writers who made a cultural impact during the Enlightenment. Click the player to begin.
Download a printable version of the interactivity.
Technology During the Enlightenment
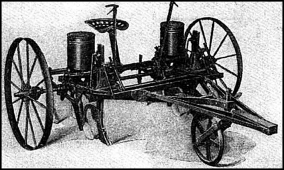
A Seed Drill
The Age of Reason also witnessed inventions and innovations in technology that stimulated trade and transportation. This is all a precursor to the Industrial Revolution!
Several new technologies developed in Europe during the Enlightenment that would have an effect on the world. Trade was one area that benefited from new technologies. Better roads were developed that could withstand all forms of weather. Better ships were also developed that could travel faster across the ocean. Both of these innovations lowered the cost of transport.
In the 1700s, there were a number of advancements in farming tools and techniques that increased agricultural production. These farming developments began in Britain and are sometimes collectively referred to as the British Agricultural Revolution. In England, a farmer by the name of Jethro Tull developed a seed drill which mechanically laid seeds at a set depth in the soil. Also, better ploughs were developed that were made from more durable materials. Inventors created a new threshing machine that reduced the number of people required to farm the land.
While these technological advancements increased the productivity of farms, landholders required fewer workers on their farms. Many of the poor had to leave the farms and seek work in the newly developing factories in Europe’s cities. In this way, the British Agricultural Revolution laid the foundation for the Industrial Revolution of the late 1700s and 1800s.
Cultural and Technological Changes of the Enlightenment Review

Now that you have explored the cultural and the technological advancements of the Enlightenment, practice what you have learned in this non-graded activity. Click the player to get started.


