RNA - Transcription, Translation, and Protein Synthesis

![]() Before you begin the scientific investigation below, make sure to download the From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report. As you complete this scientific investigation, fill in any needed information on the report template. If you need more information about each section of the report, please visit the Developmental Module.
Before you begin the scientific investigation below, make sure to download the From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report. As you complete this scientific investigation, fill in any needed information on the report template. If you need more information about each section of the report, please visit the Developmental Module.
This scientific investigation is available below or in a printable version.
Introduction
During translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the copied genetic code out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as an interpreter of the mRNA code. The tRNA matches a three-base sequence called an anticodon with the codon located on the mRNA. The tRNA then transfers the matching amino acid to the mRNA, and the amino acids are brought to the ribosome where they are connected forming a polypeptide chain.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) reads the mRNA codons and deciphers them into amino acids. Finding the amino acid sequence that forms a protein can be done by analyzing an amino acid codon wheel. The three bases make a codon. If the codon is CGU, then the first base is C, the second base is G, and the third base is U. On the codon wheel, the first base is located nearest the center, the second base is located in the middle, and the third base is located towards the outside of the wheel. Using the codon CGU, you can see from the amino acid codon wheel shown that the matching amino acid is arginine.
Objectives
In this scientific investigation, you will:
- use an amino acid codon wheel to determine the matching amino acid from a given codon.
Hypothesis
Using the Procedure and Data Collection section below, read through the procedural information for this scientific investigation. Based on your understanding of the procedure, develop your own hypotheses which describe your expected results. You should consider the following question: How will using an amino acid codon wheel help you determine the matching amino acid from a given codon? Record your hypotheses in the Hypothesis section of your From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report.
Equipment and Materials
- 2 coins
Procedure and Data Collection
- Flip two coins to determine which form of gene one your organism will inherit. Heads represents a dominant trait and tails represents a recessive trait. Use the Codes Table to determine the correct code. Record this information in the Data section of your From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report.
Codes Table
| Gene One | Dominant: TAC-GAA-TTT-CAC-ATT |
| Recessive: TAC-GAA-TAT-CCC-ATT | |
| Gene Two | Dominant: TAC – ATA – GAG – ATC |
| Recessive: TAC – AAA – GAG – ATC | |
| Gene Three | Dominant: TAC – CGG – CTC – GGT – GAG - ACT |
| Recessive: TAC – CGG – CTC – GCT – GAG - ACT | |
| Gene Four | Dominant: TAC – GTC – TCC – TTA – CAC - ATC |
| Recessive: TAC – GTC – TCA – TTA – CAC - ATC | |
| Gene Five | Dominant: TAC – GTA – GTA – AAC - ACT |
| Recessive: TAC – GTA – GGA – AAC – ACT | |
| Gene Six | Dominant: TAC – GGA – CGT – TGA – TAA - ATC |
| Recessive: TAC – GGA – CGT – TAG – TAA – ATC |
- Determine the mRNA codon from the dominant or recessive code. Record this information in the Data section of your From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report.
- Determine the tRNA anticodon from the mRNA codon. Record this information in the Data section of your From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report.
- Use the Amino Acid Codon Wheel to determine what amino acid is produced by Gene One by using the mRNA codon found in Step 2. Record this information in the Data section of your From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report.
Amino Acid Codon Wheel
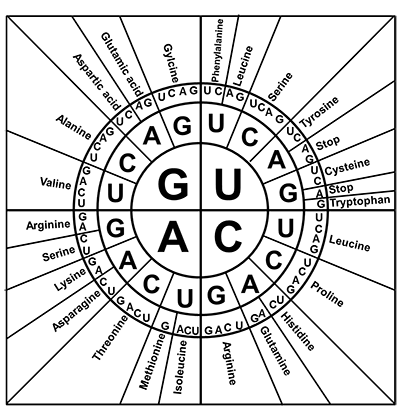
- Use the Traits Table to determine what trait is produced by the amino acid sequence for Gene One. Record this information in the Data section of your From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report.
Traits Table
| Amino Acid Sequence | Trait |
| alanine – glutamic acid – arginine - leucine | Tall |
| alanine – glutamic acid – proline - leucine | Short |
| glutamine – arginine – asparagine – valine | Full Lips |
| glutamine – serine – asparagine – valine | Thin Lips |
| histidine – histidine – leucine | Large Ears |
| histidine – proline – leucine | Small Ears |
| leucine – isoleucine – valine | Light Skin |
| leucine – lysine – valine | Dark Skin |
| proline – alanine – isoleucine – isoleucine | Large Rounded Body Shape |
| proline – alanine – threonine – isoleucine | Thin Skinny Body Shape |
| phenylalanine - leucine | Brown Eyes |
| Tyrosine – leucine | Blue Eyes |
- Repeat Steps 1-5 for the Genes Two, Three, Four, Five, and Six.
- Use the six different traits from each gene to create a drawing or sketch of your organism. Record this information in the Data section of your From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report.
Data
Use the data tables provided in the Data section of the From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report to record your data from this scientific investigation. The data tables are also shown below:
| Gene One | |
| DNA | |
| mRNA codon | |
| tRNA anticodon | |
| Amino Acid Sequence | |
| Trait | |
| Gene Two | |
| DNA | |
| mRNA codon | |
| tRNA anticodon | |
| Amino Acid Sequence | |
| Trait | |
| Gene Three | |
| DNA | |
| mRNA codon | |
| tRNA anticodon | |
| Amino Acid Sequence | |
| Trait | |
| Gene Four | |
| DNA | |
| mRNA codon | |
| tRNA anticodon | |
| Amino Acid Sequence | |
| Trait | |
| Gene Five | |
| DNA | |
| mRNA codon | |
| tRNA anticodon | |
| Amino Acid Sequence | |
| Trait | |
| Gene Six | |
| DNA | |
| mRNA codon | |
| tRNA anticodon | |
| Amino Acid Sequence | |
| Trait | |
Data Analysis
In the Data Analysis section of the From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report, provide responses to the following questions:
- How are mRNA and tRNA involved in the processes that determine the traits of your organism?
- Hypothesize what would happen if in the dominant allele of Gene Two, a substitution was made in the second mRNA codon so that it read UAA instead of UAU. What do you think would happen?
- Relate what you know about heredity to what you have learned about DNA, RNA, and proteins. What role does DNA play in how traits are inherited?
Conclusion
Using the Conclusion section of the From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report, compose three to four sentences describing an overall conclusion based on your data. Were your hypotheses true or false, and how do you know? Use the data and notes that you collected from your investigation to form your conclusion. Make sure that you include information that you gained from data analysis to support your conclusion.
Experimental Sources of Error
On your From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report, provide responses to the following questions: Are there any sources of error? If so, what are they, and what could be done to minimize error?
![]() Once you have completed the From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report, please submit your work to the dropbox.
Once you have completed the From Gene to Protein Scientific Investigation Report, please submit your work to the dropbox.