
Independence Movements in Africa
When World War II ended in 1945, there were only four countries on the African continent that were independent: Liberia, Egypt, Ethiopia and South Africa. Most of the rest were colonies under the control of Great Britain, France, Belgium and Portugal. Within the next 30 years, 47 countries won their independence. Sometimes the transition was peaceful, and sometimes it was violent, but eventually, the Europeans lost all of their territories on the continent. How did it happen so quickly?
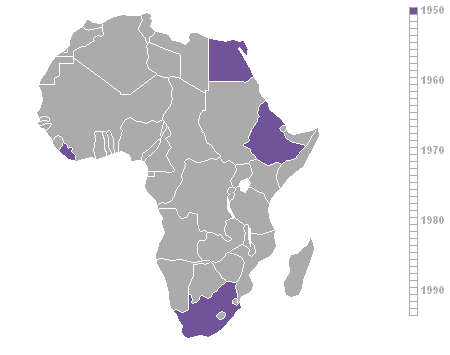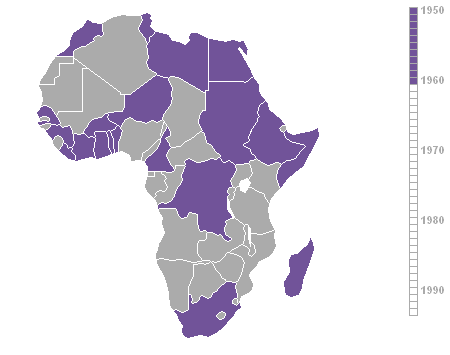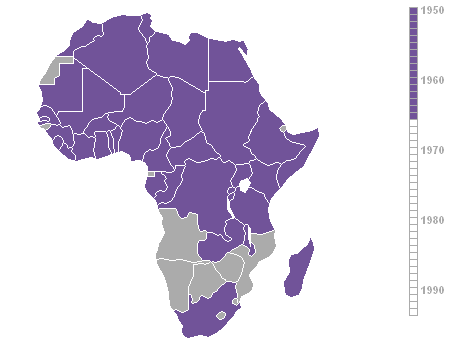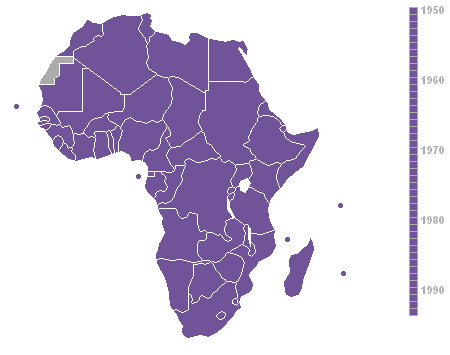
Year that African countries achieved independence (1950-93).
Map courtesy Roke.
Post WWII
After the victories of WWII, the major colonial powers faced struggles at home. The countries’ economies were in ruins, the governments deep in debt, and many of the towns and cities were destroyed. Although the colonies were important sources of wealth, maintaining control over these territories was becoming an expensive task, one that Europe couldn't afford.
The cost of maintaining control of the colonies was increasing, primarily because the colonial subjects were pushing for independence. Many of these colonial subjects had fought for the colonial powers in WWII, much as they had during WWI. When these soldiers returned home, many wanted their independence as part of their compensation for fighting in the war. This was the same situation as at the end of WWI; however, this time, the colonized nations had the force of the United Nations to back up their aspirations of freedom.
The United Nations
The United Nations was established in 1945 at the end of WWII. Its charter firmly established the right of all people to self-determination, or the right to establish their own government free from the influence of any other country. This right was considered so important that it appeared in the very beginning of the document. Chapter 1, Article 1, part 2 of the U.N. charter states that one of the four main purposes of the U.N. is:
To develop friendly relations among nations based on respect for the principle of equal rights and self-determination of peoples, and to take other appropriate measures to strengthen universal peace;
African Independence Movements

With the U.N. on their side and Europe's power on the decline, Africa's colonial subjects began a successful push for independence that would sweep the continent. View this presentation to learn about their struggles as well as some of the important people and events in African independence movements. Click the player to begin.
Download a printable version of the interactivity.
Independence Movements in Africa Review

Now that you have explored independence movements in Africa, practice what you have learned in this interactivity. Read each question and select the appropriate answer. Click the player to get started.


