Cellular Membranes
Cell Size
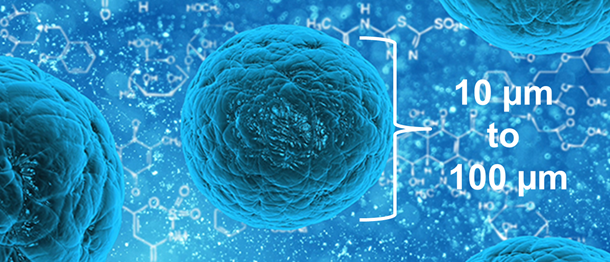
Take a look at the size of the period at the end of this sentence. Most cells are smaller than that period. Instead of being measuring cells in units of centimeters or millimeters, scientists measure cells in units of micrometers (µm). Many cells are less than 100 µm (100 x 10-6 m) in diameter, and some, like the red blood cell at 10 µm, are even smaller.
![]() To compare the relative sizes of different types of cells and cellular structures, explore Cell Size and Scale from the University of Utah. Use the slider below the picture to zoom in and take a look at the different types of particles and cells. How do they compare to the largest object in the picture, which is the coffee bean?
To compare the relative sizes of different types of cells and cellular structures, explore Cell Size and Scale from the University of Utah. Use the slider below the picture to zoom in and take a look at the different types of particles and cells. How do they compare to the largest object in the picture, which is the coffee bean?
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
 The size of a cell determines how efficiently the cell can function. Larger cells have a larger surface area to volume ratio. This causes larger cells to create more waste and use more energy when taking in and expelling nutrients and waste through its cell membrane. The surface area to volume ratio limits how large a cell can become. If a cell becomes too large, it will not be able to function properly. In this interactivity, learn about the importance of a cell’s surface area to volume ratio. Click the player button to begin.
The size of a cell determines how efficiently the cell can function. Larger cells have a larger surface area to volume ratio. This causes larger cells to create more waste and use more energy when taking in and expelling nutrients and waste through its cell membrane. The surface area to volume ratio limits how large a cell can become. If a cell becomes too large, it will not be able to function properly. In this interactivity, learn about the importance of a cell’s surface area to volume ratio. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of the interactivity.
Structure of the Cell Membrane
 What are the parts of a cell membrane? The cell membrane is a combination of phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. Combined, these substances form a protective bilayer that is selectively permeable. This extremely important part of the cell allows substances to enter and exit the cell. The cell membrane keeps the cell balanced and functioning properly. In this interactivity, explore the structure of the cell membrane. Click the player button to begin.
What are the parts of a cell membrane? The cell membrane is a combination of phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. Combined, these substances form a protective bilayer that is selectively permeable. This extremely important part of the cell allows substances to enter and exit the cell. The cell membrane keeps the cell balanced and functioning properly. In this interactivity, explore the structure of the cell membrane. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of the interactivity.
Processes of the Cell Membrane
 Cell membranes are selectively permeable. This means that cells permit only certain materials to pass into and out of the cell without interference. The movement of molecules will occur until a cell reaches equilibrium with its environment. This allows the cell to maintain homeostasis. Through a multitude of special processes, various substances pass through the cell membrane, some of which require assistance, while other substances pass through unaided. In this interactivity, investigate the processes involved with the cell membrane. Click the player button to begin.
Cell membranes are selectively permeable. This means that cells permit only certain materials to pass into and out of the cell without interference. The movement of molecules will occur until a cell reaches equilibrium with its environment. This allows the cell to maintain homeostasis. Through a multitude of special processes, various substances pass through the cell membrane, some of which require assistance, while other substances pass through unaided. In this interactivity, investigate the processes involved with the cell membrane. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of the interactivity.
Concentration States Effect on Cells
 Before you can learn about the processes involved with the cell membrane. You need to understand why molecules will move based on the concentration gradient and the three different concentration states. In this interactivity, learn why different concentrations exist and create a concentration gradient. Knowing this information will help you understand the processes involved with the cell membrane. Click the player button to begin.
Before you can learn about the processes involved with the cell membrane. You need to understand why molecules will move based on the concentration gradient and the three different concentration states. In this interactivity, learn why different concentrations exist and create a concentration gradient. Knowing this information will help you understand the processes involved with the cell membrane. Click the player button to begin.
View a printable version of the interactivity.
Demonstrating Diffusion

![]() To demonstrate the principles of diffusion, grab a glass and fill it with ordinary tap water, then slowly pour in a packet of your favorite powdered drink mix. Do not stir in the powdered drink mix, but watch it closely. At first, you will observe that some of the drink mix sits on top of the water, and some of it slowly drops to the bottom of the glass. However, over the next several minutes, you will notice that the mix slowly dissolves and diffuses throughout the water, changing the clear water into the color of the drink mix powder.
To demonstrate the principles of diffusion, grab a glass and fill it with ordinary tap water, then slowly pour in a packet of your favorite powdered drink mix. Do not stir in the powdered drink mix, but watch it closely. At first, you will observe that some of the drink mix sits on top of the water, and some of it slowly drops to the bottom of the glass. However, over the next several minutes, you will notice that the mix slowly dissolves and diffuses throughout the water, changing the clear water into the color of the drink mix powder.
The drink mix will eventually diffuse throughout the glass of water. The molecules of water are in constant motion, bouncing in random directions off of one another and the molecules in the powdered drink mix. Over time, this random motion causes the molecules in the powdered drink mix to spread throughout the water, which you can see happening as the solution slowly gets darker and darker in color.
Eventually, the concentration of powdered drink mix molecules spreads equally throughout the entire container of water. Of course, you normally speed up this process when your stir the mixture. The mixture reaches equilibrium when the molecules of powdered drink mix and the molecules of water are in balance.
In Da Club - Membranes and Transport
![]() The movement of substances in and out of the cell membrane is essential to a cell’s ability to maintain homeostasis. Some transport processes require an additional input of energy, and some do not. Together, these processes function to keep the cell healthy. View from In Da Club – Membranes and Transport from eMediaVASM to review how cells regulate their contents and communicate with one another via mechanisms within the cell membrane.
The movement of substances in and out of the cell membrane is essential to a cell’s ability to maintain homeostasis. Some transport processes require an additional input of energy, and some do not. Together, these processes function to keep the cell healthy. View from In Da Club – Membranes and Transport from eMediaVASM to review how cells regulate their contents and communicate with one another via mechanisms within the cell membrane.
Cellular Membranes Review
![]()
 Now that you investigated cellular membranes, review your knowledge. In this non-graded activity, read each question and select the correct response. Then, click SUBMIT to check your answer. Click the player button to get started.
Now that you investigated cellular membranes, review your knowledge. In this non-graded activity, read each question and select the correct response. Then, click SUBMIT to check your answer. Click the player button to get started.