Cellular Membranes
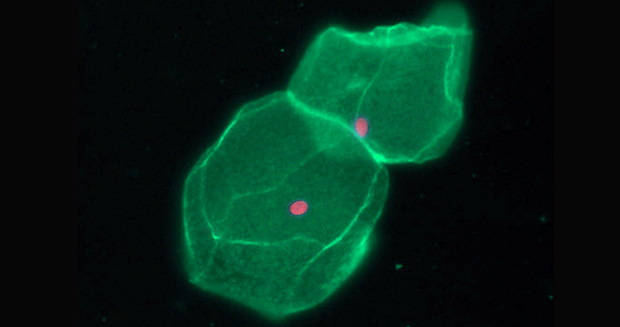
The plasma membrane and nucleus in bladder cells
The cell membrane protects the cell from its external environment. The cell membrane is a fluid mosaic, composed of phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. Acting as a semi-permeable, protective barrier, the membrane allows some molecules to enter the cell and keeps some molecules out. The transport of molecules in and out of the cell is important to the cell’s ability to maintain homeostasis. Diffusion and osmosis are types of passive transport that do not require any energy from the cell. Active transport requires additional energy.




